FIGURE 5.
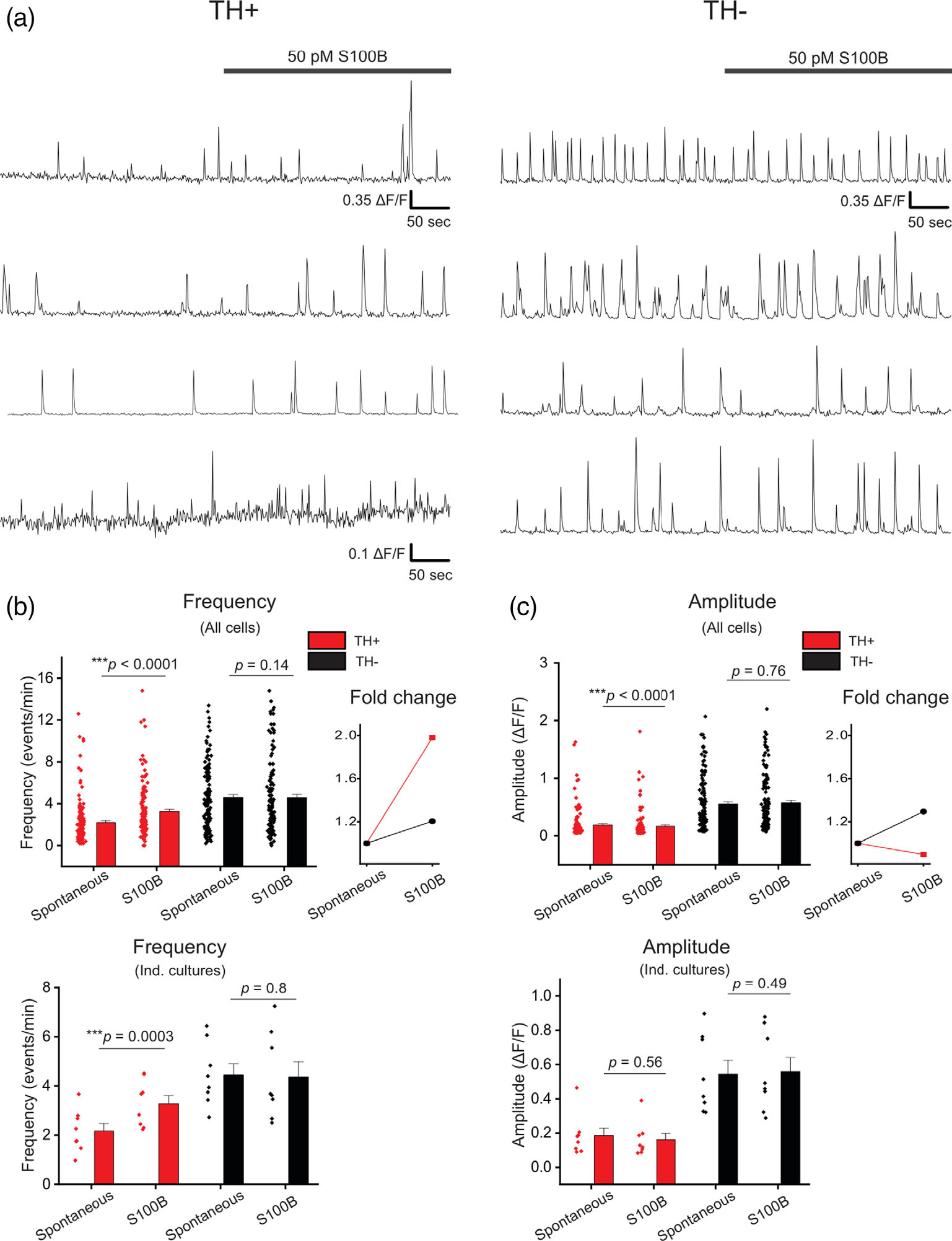
Acute exposure of primary midbrain cultures to S100B peptide increases spontaneous Ca2+ flux frequency only in TH+ neurons. (a) Multiple representative traces of spontaneous Ca2+ fluxes in TH+ and TH− neurons with acute bath application of 50 pM S100B peptide are shown. (b) A graph with average frequency of Ca2+ flux events from individual TH+ (red) and TH− (black) neurons with and without S100B peptide is shown. The line graph on the right shows the average fold change of Ca2+ flux frequency for TH+ and TH− cells following S100B application. The graph below shows the average frequency of TH+ and TH− neurons binned by week of culture. (c) A graph with average amplitude of Ca2+ events from individual TH+ (red) and TH− (black) neurons with and without S100B peptide. The line graph on the right shows the average fold change of Ca2+ flux amplitude for TH+ and TH− cells following S100B application. The graph below shows the average amplitude of TH+ and TH− neurons binned by individual culture. n = 137 for TH+ neurons and 134 for TH− neurons from eight independent cultures. All errors are SEM; p-values for all cells are based on Wilcoxon signed rank tests for TH+ spontaneous, TH+ S100B and TH− spontaneous, TH− S100B and Mann–Whitney tests for TH+ spontaneous, TH− spontaneous; p-values for individual cultures are based on paired sample t tests for TH+ spontaneous, TH+ S100B and TH− spontaneous, TH− S100B, and two sample t tests for TH+ spontaneous, TH− spontaneous
