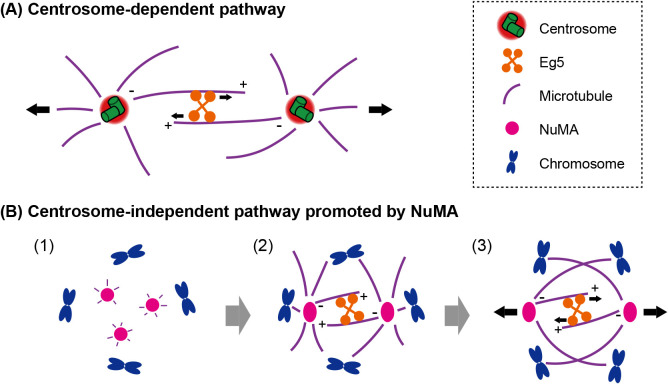
Fig. 2.
Models for two pathways that promote spindle bipolarization in human cells. (A) The canonical centrosomal pathway. At G2/M transition, the two centrosomes are pushed apart by the plus-end-directed motor activity of kinesin Eg5. (B) The NuMA-mediated pathway, which occurs independently of centrosomes. (1) At the onset of mitosis, NuMA aggregates and organizes microtubule asters. (2) Dynein activity and the clustering activity of NuMA assembles the NuMA aggregates into two poles; subsequently, Eg5 is loaded onto the antiparallel microtubules. (3) Spindle poles are separated through Eg5 motor activity and kinetochore-microtubule attachments.