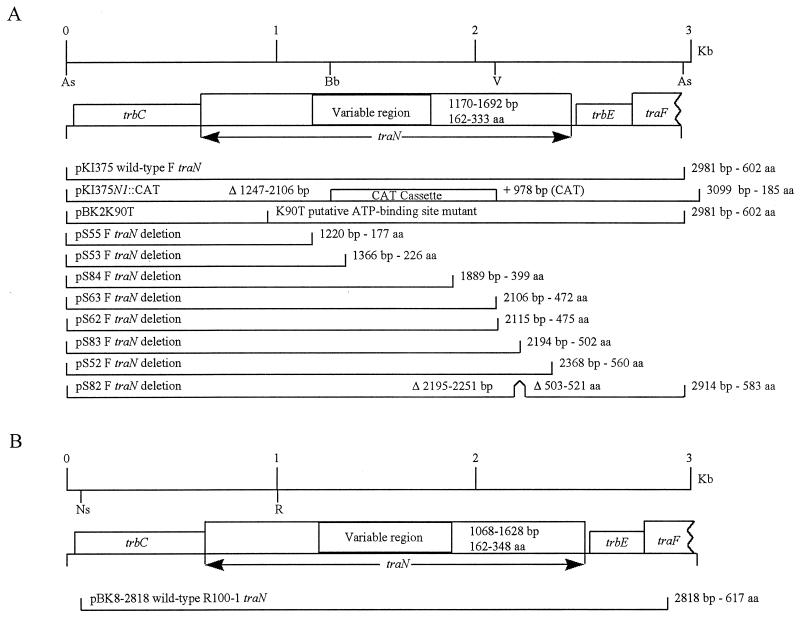
FIG. 1.
Physical maps of the various F constructs used in this study. (A) F plasmid derivatives. (B) R100-1 plasmid derivatives. The region corresponding to the F or R100-1 plasmid from which each of these constructs is generated is shown; sizes are marked at the top. Restriction enzymes: As, Asp7001; Bb, BbrPI; Ns, NsiI; R, EcoRI; V, EcoRV. tra and trb genes are boxed. The variable region in TraN is also boxed, and the range of amino acids that this region represents in F and R100-1 TraN is shown. Each construct is shown approximately to scale, and the length of the insert in pBS is shown along with the number of expected amino acids remaining in TraN. The F plasmid deletions are all derivatives of the initial clone of F traN, pKI375, which is a 3-kb Asp7001 fragment of the F plasmid cloned into pBS KS+/EcoRV (25). The R100-1 traN clone is a derivative of a 3.5-kb NsiI fragment of R100-1 cloned into pBS SK+/PstI and subsequently treated with exonuclease to generate a deletion. pS82 is an in-frame deletion of 18 aa. T7 RNA polymerase-directed transcription proceeds from left to right in both diagrams. The region replaced by the CAT cassette in pKI375N1::CAT is boxed. The K90T mutation is a Lys-to-Thr mutation at residue 90 in TraN.