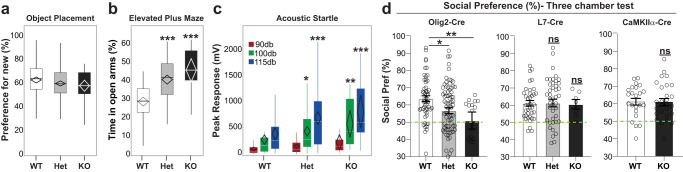
Fig. 7. Mice with oligodendrocyte specific Anks1b deletion display behavioral deficits associated with ASD.
a Neither Olig2-Het nor Olig2-KO mice show learning deficits in the object placement test, a hippocampus-dependent memory assay. All 3 groups averaged above a passing score (>50% preference for new location) using a 40-minute retention interval. b Olig2-Het and Olig2-KO mice showed a robust reduction in avoidance behaviors compared to WT controls, spending more time in the open arms as a percentage of total time in open and closed arms of an elevated plus maze (but see Supplementary Fig. 8d). One-way ANOVA. c Peak magnitude of the acoustic startle reflex is robustly increased in Olig2-Het and Olig2-KO mice at 100db and 115db. (*p = 0.0334, **p = 0.00281). d In the three-chamber test, (left) Olig2-Het and Olig2-KO mice show significantly reduced and borderline preference for a conspecific mouse over an inanimate object (One-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s post hoc, WT vs Het: p = 0.0174; WT vs KO: p = 0.0077. This reduction in social preference was not observed in mice with Anks1b deletion from (middle) cerebellar Purkinje cells (L7-Het and L7-KO) or (right) forebrain specific excitatory neurons (Camk2a-KO). Dotted green line indicates 50% preference. a–c Box plots show 25th–75th quantiles (box), median (black line), 95% confidence intervals (diamond), and range (black whiskers). Bar graphs in d show mean ± s.e.m. with all data points shown. For Anks1b Olig2-Het and Olig2-KO experiments, n = 53 WT, 82 Het, 15 KO (two measurements made for object placement). For L7-Het and L7-KO experiments, n = 38 WT, 44 Het, 7 KO. For Anks1b Camk2a-KO experiments, n = 23 WT, 27 KO. No significant sex differences were observed in any behaviors evaluated. If 2-way ANOVA showed significant main effect of genotype, post hoc 2-sided Student’s t test was performed, *, **, ***p < 0.05, <0.005, <0.0005. All significant results show high power (b > 0.85). For social preference test in Olig2-Het and Olig2-KO statistical power b > 0.95. Source data for all panels are provided as a Source Data file.