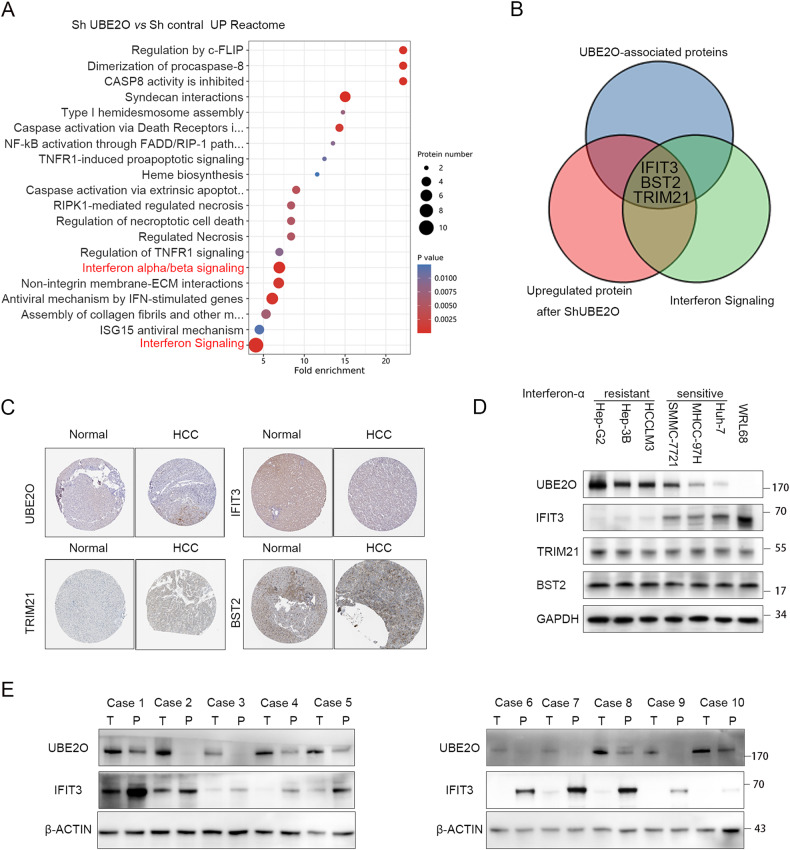
Fig. 1. UBE2O negatively regulates IFIT3 expression in HCC.
A Cells stably transduced with Sh-UBE2O were established using lentiviral transduction, and proteomic analysis was performed with controls. Reactome enrichment analysis was performed with the upregulated differentially expressed proteins. Reactome enrichment analysis was performed with the ReactomePA R package. B Immunoprecipitation was conducted in HCCLM3 cells using an anti-UBE2O antibody, and the samples were sent for mass spectrometry analysis to identify proteins bound to UBE2O (indicated by blue circles). Proteins upregulated after UBE2O knockdown are indicated by red circles, while those involved in the interferon pathway are indicated by green circles. The proteins overlapping among these three groups were identified as IFIT3, BST2, and TRIM21. C The expression of UBE2O, IFIT3, TRIM21, and BST2 was queried in the HPA database. UBE2O and IFIT3 exhibited opposing expression trends; UBE2O was highly expressed, but IFIT3 was expressed at low levels in HCC tissues, whereas normal liver tissue showed low expression of UBE2O and high expression of IFIT3. Both UBE2O and TRIM21, as well as BST2, displayed similar trends, with high expression observed in HCC tissues but low expression observed in normal liver tissues. D In HCC cell lines, UBE2O was highly expressed in tumor cells and expressed at low levels in normal cells. In contrast, IFIT3 was expressed at low levels in tumor cells and highly expressed in normal hepatocytes (n = 3). Cell lines with low UBE2O combined with high IFIT3 are interferon-α sensitive, whereas cells with high UBE2O combined with low IFIT3 are interferon-resistant. E The protein expression levels of UBE2O and IFIT3 were determined in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 3).