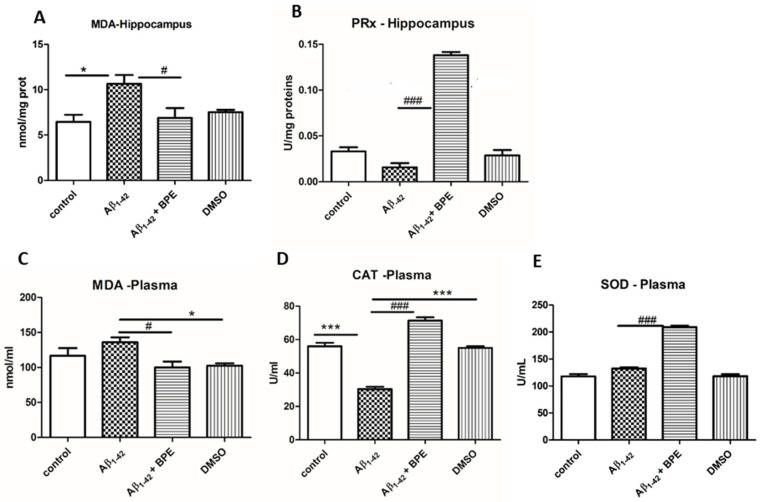
Figure 4.
The effects of BPE administration on malondialdehyde (MDA) levels (A,C) and on peroxidase (PRx) (B), catalase (CAT) (D), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) (E) activities in the hippocampus and plasma of rats. BPE administration decreased lipid peroxidation in the hippocampus and plasma (Aβ1-42 + BPE vs. Aβ1-42, p < 0.05) (A,C). Significantly higher levels of MDA were recorded in the hippocampus and plasma of the Aβ1-42-treated group (Aβ1-42 vs. control, p < 0.05) (A); Aβ1-42 vs. DMSO, p < 0.05 (C). In the hippocampus, PRx displayed higher activity after BPE treatment (Aβ1-42 + BPE vs. Aβ1-42, p < 0.001) (B). In the plasma, both CAT and SOD increased after BPE treatment (Aβ1-42 + BPE vs. Aβ1-42, p < 0.001) (D,E). CAT displayed lower levels than either control or DMSO group after Aβ1-42 treatment (Aβ1-42 vs. control/DMSO, p < 0.001) (D). Each group consisted of 7 rats. Aβ1-42 vs. control/DMSO, *; Aβ1-42 vs. Aβ1-42 + BPE, #. Results are expressed as mean ± SD; #,*, p < 0.05; ###, ***, p < 0.001.