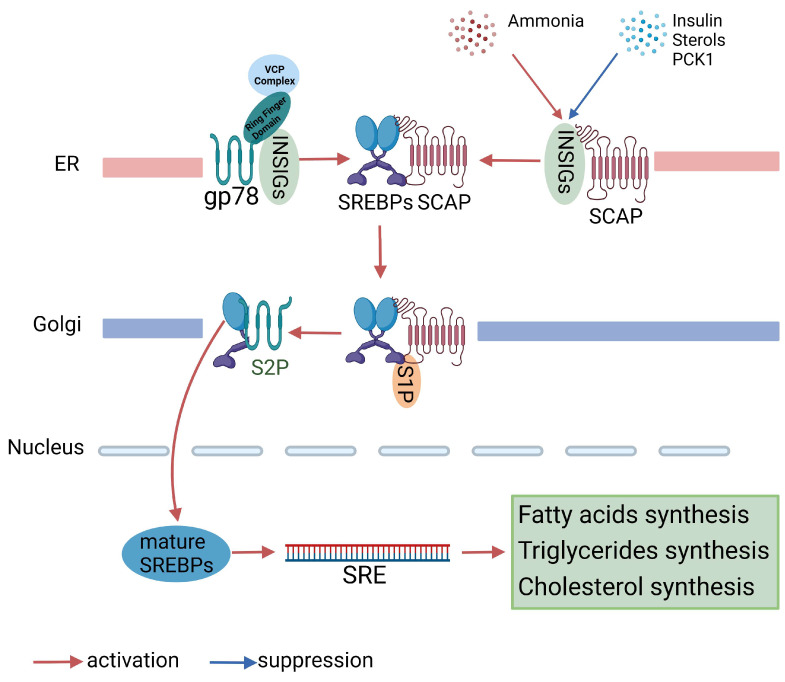
Figure 1.
Proteolytic activation of SREBPs. Under basal conditions, SREBPs are complexed with SCAP, INSIGs, and gp78 in the ER membrane to prevent their activation. However, various stimuli, such as sterols, insulin, ammonia, and PCK1, can trigger INSIGs’ degradation, allowing the SREBP-SCAP complex to translocate from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. Within the Golgi, the SREBP is cleaved in a two-step proteolytic mechanism by S1P and S2P. The resulting mature SREBP can then enter the nucleus, where it binds to SRE promoters and activates the transcription of genes involved in fatty acid, triglyceride, and cholesterol synthesis. Please refer to the list of abbreviations for the abbreviations mentioned in this figure.