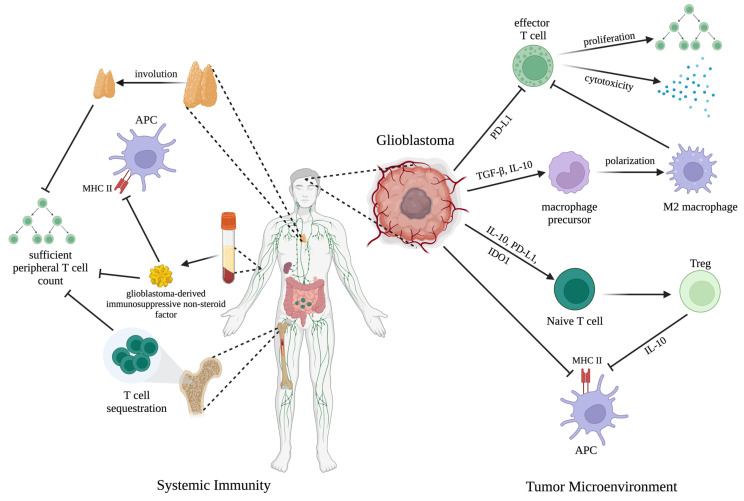
Figure 1.
Key glioblastoma immune escape mechanisms mentioned in this review. The efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is critically dependent on an intact host immune system in both the tumor microenvironment (TME) and systemic landscape. Glioblastoma fosters an immunosuppressive environment by targeting multiple aspects of host immunity that typically should prevent cancer progression. In the tumor microenvironment, glioblastoma interferes with antigen presentation, promotes M2 macrophage polarization and Treg formation, and directly impedes T-cell cytotoxicity and proliferation. In systemic immunity, glioblastoma is associated with thymic involution and T-cell sequestration in the bone marrow. An immunosuppressive non-steroid factor further disrupts peripheral T-cell function and also impairs antigen presentation. Mechanisms of action are further described in the respective sections of this review. This figure was created with BioRender.com, access date 15 November 2023.