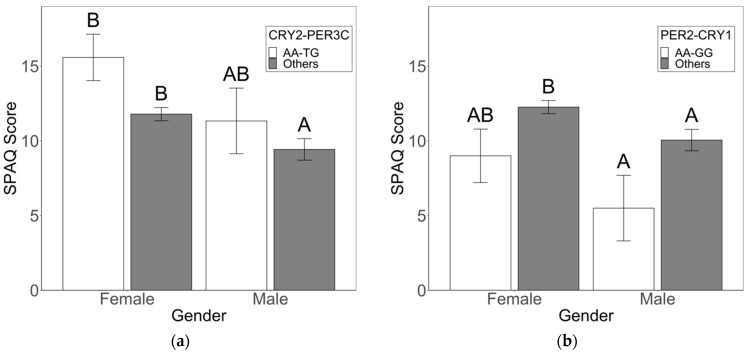
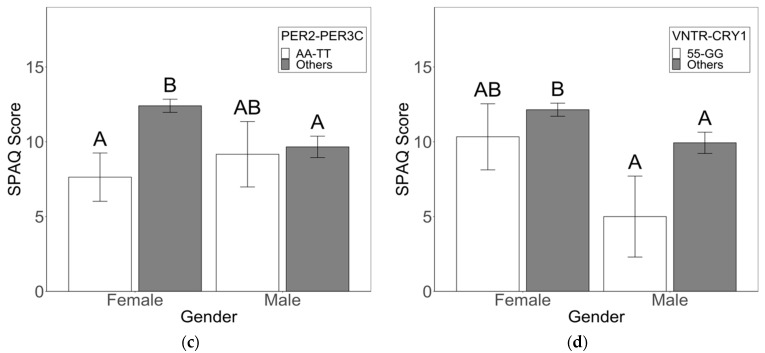
Figure 3.
Two-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc analysis reveal risk and protective combinations for seasonality in females. (a) Significantly higher average SPAQ scores were identified in females with the CRY2-AA/PER3C-TG combination relative to other genotypic combinations (Genotype: F1,217 = 4.084, p = 0.044; Gender: F1,217 = 5.496, p = 0.020; Genotype × Gender: F1,217 = 0.449, p = 0.504). (b) Average SPAQ scores were lower for males and females with the PER2-AA/CRY1-GG combination (Genotype: F1,217 = 7.001, p = 0.009; Gender: F1,217 = 3.735, p = 0.055; Genotype × Gender: F1,217 = 0.192, p = 0.662). (c) Average SPAQ scores were lower for females with the PER2-AA/PER3C-TT combination than for females with other combinations (Genotype: F1,217 = 3.420; p = 0.066, Gender: F1,217 = 0.182; p = 0.670, Genotype × Gender: F1,217 = 2.257, p = 0.134). (d) Average SPAQ scores were lower for males and females with VNTR-5,5/CRY1-GG combination (Genotype: F1,217 = 3.525, p = 0.062; Gender: F1,217 = 4.417, p = 0.037; Genotype x Gender: F1,217 = 0.755, p = 0.396) (N = 221). A, B denote significant differences for Tukey post hoc analyses.