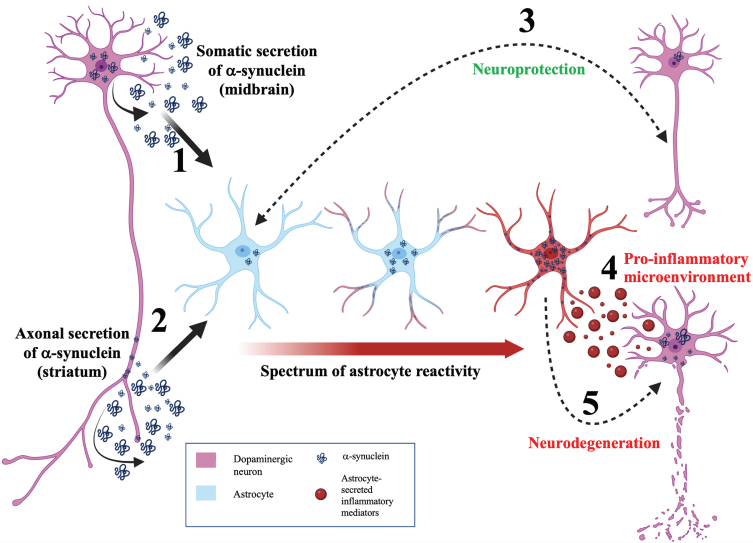
Fig. 2.
A neuroinflammatory model for astrocytic α-synuclein determining the balance between neuroprotection and neurodegeneration. Model schematic depicting a neuroinflammatory role for astrocytes in maintaining the balance between neuroprotection and neurodegeneration during PD. (1) α-synuclein is secreted by the soma of neurons and internalized by astrocytes. This somatodendritic neuron-astrocyte coupling may be seen in the midbrain. (2) α-synuclein is externalized by the axon of neurons and internalized by astrocytes. This morphological coupling may be seen in the striatum. (3) Bidirectional, efficient transfer of α-synuclein between astrocytes and neurons facilitates neuroprotection. (4) Aberrant α-synuclein accumulation induces astrocyte reactivity. Depending on the load of α-synuclein in the astrocyte, astrocyte reactivity can range from mild (blue astrocyte) to moderate (astrocyte with red process tips) to severe reactivity (red astrocyte). (5) Highly reactive astrocytes will secrete cytokines (red vesicles) resulting in a pro-inflammatory microenvironment and consequent neurodegeneration. In addition, transfer of α-synuclein from astrocytes to neurons can induce neurodegeneration.