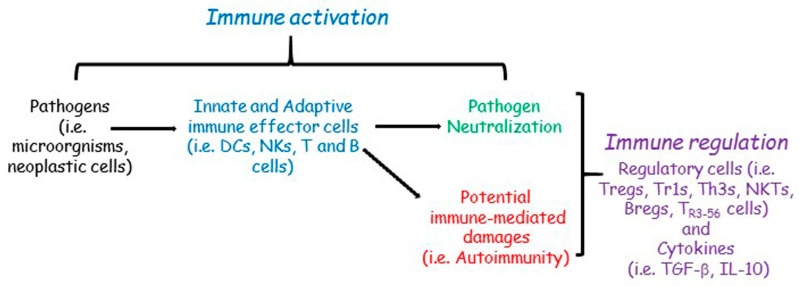
Figure 2.
Simplified immune plasticity network. Pathogens activate the innate and adaptive immune effector cells (dendritic cells, DCs; natural killers, NKs; T and B cells) that induce pathogen neutralization during the immune activation phase. However, immune activation could also exert potential immune-mediated damage as a sort of side effect. The immune regulation phase (T regulatory cells, Tregs; Type 1 regulatory cells, Tr1s; T helper 3 cells, Th3s; natural killer T cells, NKTs; B regulatory cells, Bregs; T CD3+ CD56+ regulatory cells, TR3-56 cells; transforming growth factor beta, TGF-β; interleukin 10, IL-10) modulates immune activation and avoids immune-mediated damages.