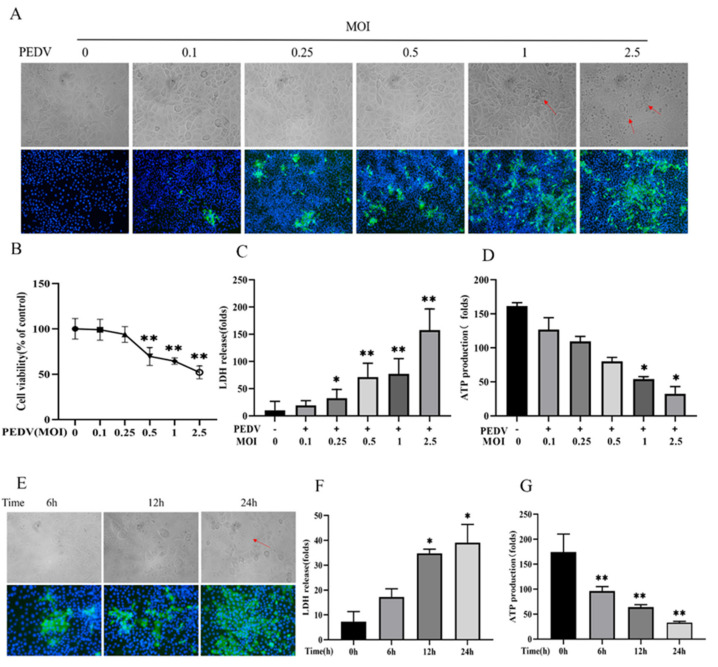
Figure 1.
WEPO attenuated PEDV-infected Vero cell injury. (A) Morphological observation and immunofluorescence of Vero cells infected with different concentrations of PEDV (The magnification of a microscope is 200 times. The area indicated by the red arrow is the vacuole formed after Vero cell lesion). (B) The cytotoxicity of PEDV in Vero cells. Cells were treated with PEDV at an MOI of 0 to 2.5 for 24 h, and cell survival was detected by CCK-8 assay. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). ** p < 0.01 vs. control. (C) The release of LDH was measured after Vero cells were infected with different concentrations of PEDV. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. control. (D) The amount of ATP production was measured after Vero cells were infected with different concentrations of PEDV. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05 vs. control. (E) Morphological observation and immunofluorescence after Vero cells were infected with PEDV at different times (6 h, 12 h, 24 h). (F) LDH release was detected after PEDV infection of Vero cells for different periods. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05 vs. control. (G) The amount of ATP production was measured after PEDV infection of Vero cells at different times. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). ** p < 0.01 vs. control.