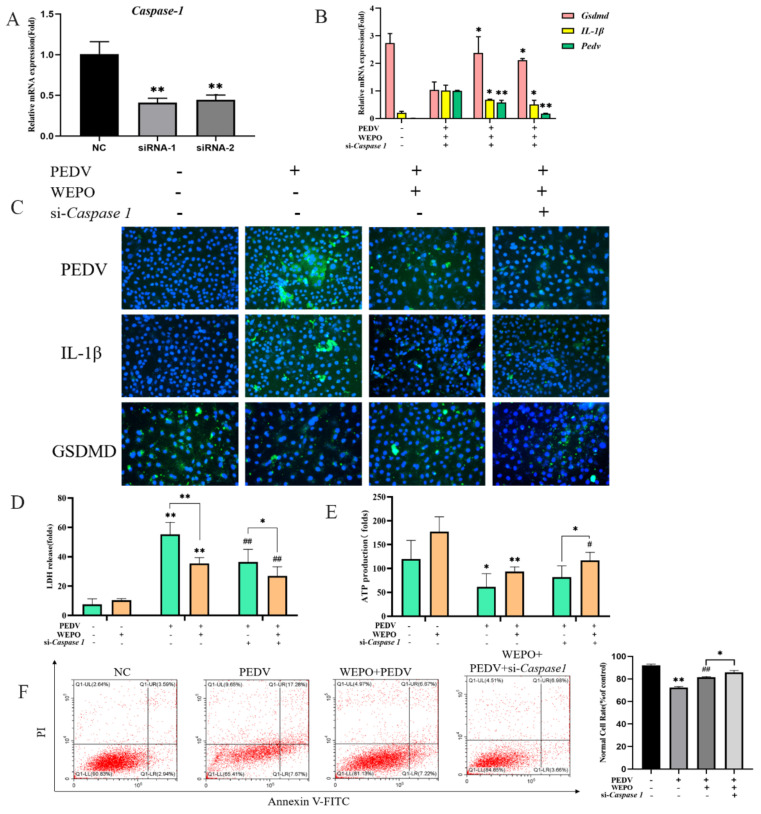
Figure 5.
Caspase-1 is needed for GSDMD-N induction and WEPO pyroptosis in response to PEDV infection. (A) Detection of the interference efficiency of si-Caspase-1 by RT-PCR. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). ** p < 0.01 vs. control. (B) Caspase-1 was knocked out, and IL-1β, GSDMD, and PEDV expression levels were detected using RT-PCR. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. positive control (PEDV + WEPO). (C) Expression of PEDV, GSDMD, and IL-1β after Caspase-1 knockout using an immunofluorescence assay. (The magnification of a microscope is 200 times). (D) Detection of LDH release after adding PEDV followed by adding purslane and knocking off Caspase-1. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05. ** p < 0.01 vs. control. ## p < 0.01 vs. positive control (PEDV). (E) Detection of ATP generation after adding PEDV followed by adding purslane and knocking out Caspase-1. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. control. # p < 0.05 vs. positive control (PEDV). (F) Detection of apoptosis in Vero cells after knocking out Caspase-1 by flow cytometry. * p < 0.05. ** p < 0.01 vs. control. ## p < 0.01 vs. positive control (PEDV).