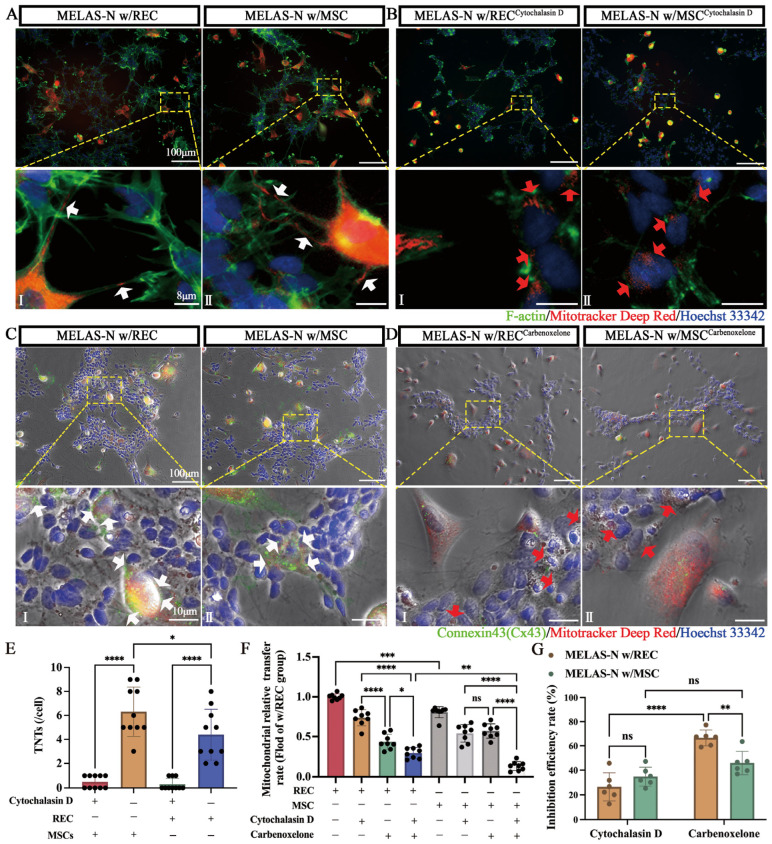
Figure 3.
MSCs/RECs connect with MELAS neurons (MELAS-N) via TNTs and Cx43-containing GJCs. (A) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of MELAS neurons co-cultured with RECs (I) or MSCs (II). (B) Representative images of MELAS neurons co-cultured with RECs (I) or MSCs (II) after the addition of cytochalasin D. Mito-Red labeled RECs or MSCs, Hoechst33342 labeled MELAS neurons, and F-actin labeled all the cells. White arrowheads: REC/MSC mitochondria in TNTs. Red arrows: REC/MSC mitochondria were present in MELAS neurons, even without TNT formation. (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of MELAS neurons co-cultured with RECs (I) or MSCs (II). (D) Representative images of MELAS neurons co-cultured with REC (I) or MSC (II) after the addition of carbenoxelone. Mito-Red labeled REC or MSC, Hoechst33342 labeled MELAS neurons, and Connexin43 labeled all cells. White arrows indicate high Cx43 expression at the cell junctions. Red arrows indicate reduced Cx43 expression after gap junction inhibition, but REC/MSC mitochondria are still present in the MELAS neurons. (E) The number of TNTs in cells from each group was calculated with or without cytochalasin D (n = 10). (F) Quantification of mitochondrial transfer rate of RECs/MSCs to MELAS neurons in response to inhibitors (cytochalasin D and carbenoxelone) (n = 8). (G) Inhibitory efficacy of different inhibitors on REC/MSC mitochondrial transfer rate (n = 6). Data represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. ns, not significant. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.