Fig. 4.
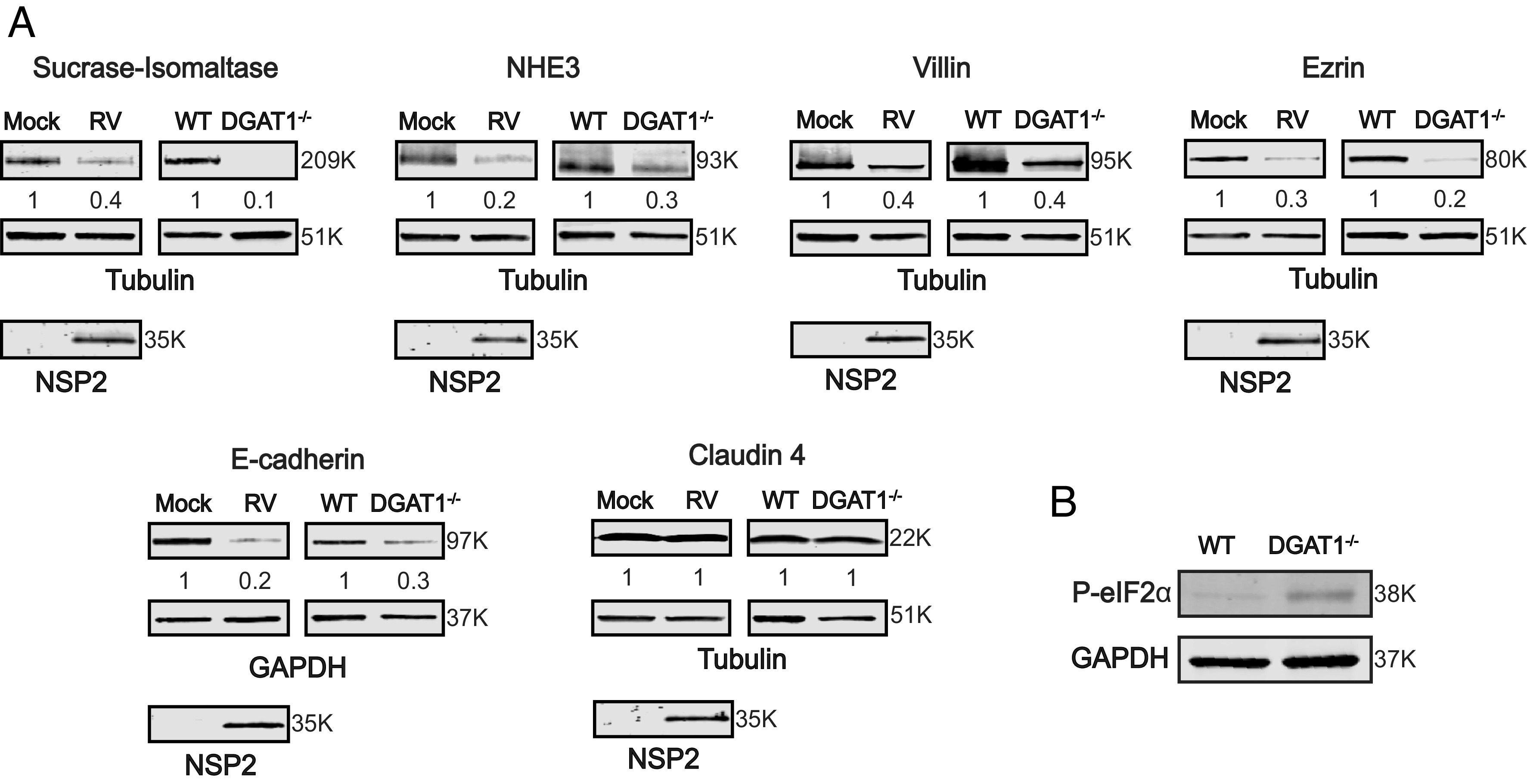
RV-mediated DGAT1 degradation or DGAT1 deficiency in HIEs leads to loss of expression of apical brush border enzymes, cytoskeleton-binding proteins, and tight junctional proteins. (A) 3D HIEs were mock- or Ito-infected at a MOI of 10 and harvested at 24 hpi. Western blots of cell lysates prepared from mock- and RV-infected HIEs, and parental and DGAT1−/− HIEs, were probed with antibody to detect the indicated proteins. Tubulin or GAPDH were detected as loading controls and NSP2 detected to indicate RV infection. The primary antibodies were detected with secondary antibodies conjugated to IRDye680RD and IRDye800CW. Infrared images of immunoblots were acquired using the Odyssey CLx and analyzed using Image Studio Lite software. Quantification of proteins normalized to tubulin or GAPDH with mock or WT set at 1 (n = 3) is shown below the respective blots. Molecular weights are indicated to the right of each blot. (B) Western blot of lysates from WT and DGAT1−/− HIEs demonstrating a basal increase in P-eIF2α in the DGAT1−/− HIEs.
