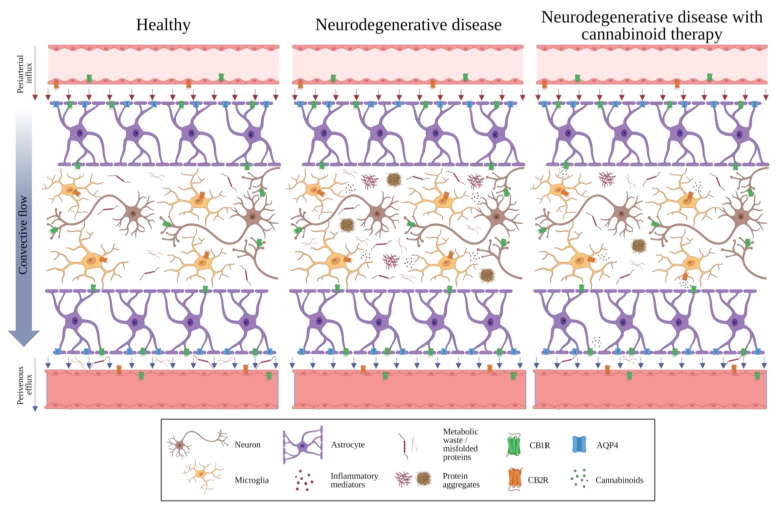
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the blood-brain barrier, the glymphatic system, and the endocannabinoid system under 3 different conditions. Healthy: Interconnected regulation of CNS homeostasis under normal conditions. The BBB forms a protective barrier between the bloodstream and the brain, comprising tightly packed endothelial cells, pericytes, and astrocytic endfeet. This selective barrier strictly regulates the passage of molecules into and out of the brain, maintaining optimal microenvironmental conditions. The GS operates as a CSF and ISF drainage network where specialized perivascular spaces enable the efficient clearance of metabolic waste products and neurotoxic substances, ensuring effective waste management and maintaining brain homeostasis. Cannabinoid receptors (CB1R and CB2R) are strategically located on neurons, astrocytes, and microglia, allowing for versatile regulation of CNS functions. Neurodegenerative disease: The GS experiences impaired drainage and clearance mechanisms, leading to the accumulation of metabolic waste, toxic proteins, and inflammatory mediators. Neurodegenerative disease with cannabinoid therapy: In neurodegenerative conditions under cannabinoid treatment, the GS showcases improved drainage and clearance mechanisms, promoting the efficient removal of metabolic waste and toxic proteins. Simultaneously, the ECS reflects a restored balance and a reduction of inflammatory mediator synthesis. Abbreviations: AQP4, Aquaporin-4 water channel; CB1R, Cannabinoid receptor 1; CB2R, Cannabinoid receptor 2. This figure was created with BioRender.com, agreement number YJ265GYS33, 28 November 2023.