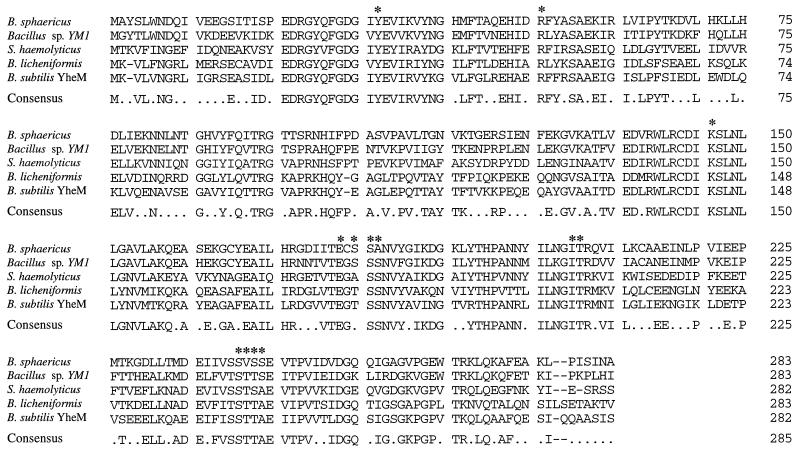
FIG. 2.
Primary sequence homology between the d-amino acid transaminase, other known microbial d-amino acid transaminases, and the gene product of the B. subtilis yheM gene. The consensus sequence shows the amino acids that are conserved in three or more sequences. Individual percentages for sequence conservation with B. sphaericus d-amino acid transaminase are as follows: Bacillus sp. strain YM1, 67%; S. haemolyticus, 48%; B. licheniformis, 42%; and B. subtilis YheM, 42%. Asterisks indicate residues assigned active functions in the YM1 enzyme (29): substrate-cofactor proton transfer (K145), cofactor ion pairing (Y31, R50, E177, S179 to S181, I204, and T205), and substrate side chain recognition (S240 to S243).