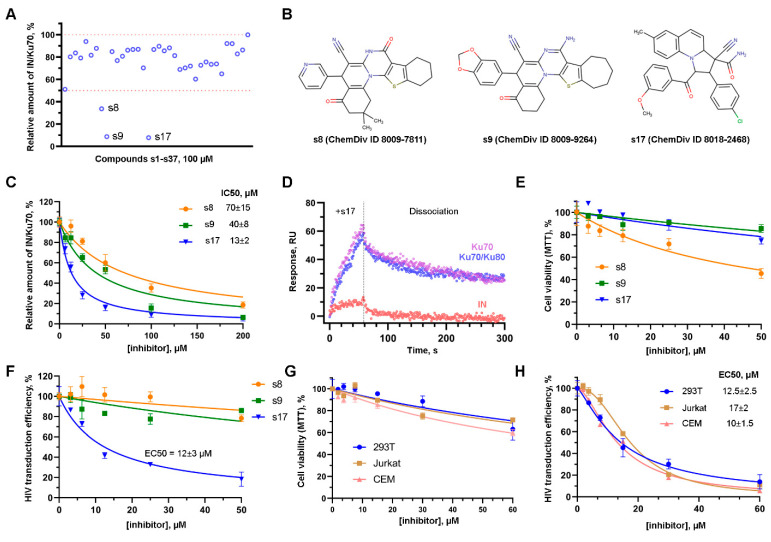
Figure 1.
The effect of small molecules on the formation of the IN/Ku70 complex and on HIV-1 early replication events. (A) The effect of 100 μM compounds s1–s37 preselected with molecular docking procedure on the ability of Ku70 to bind HIV-1 IN in vitro. Mean values (n = 3) are shown. (B) Structures of the three most active compounds. (C) The effect of increasing concentrations of s8, s9, and s17 on the Ku70/IN complex formation in vitro. Mean values ± SD (n = 3) are shown. (D) SPR sensograms of the s17 interaction with His6-tagged HIV-1 IN, Ku70 protein, and Ku70/Ku80 heterodimer immobilized on the HTE sensor chip. The mean value of two independent experiments for each time point is shown. (E) The effect of s8, s9, and s17 on cell viability. 293T cells were treated with indicated concentrations of the compounds for 24 h. MTT assay was performed to measure cell viability. Mean values ± SD (n = 3) are shown. (F) The effect of s8, s9, and s17 on 293T cells transduction with HIV_wt. 293T were transduced with firefly luciferase coding HIV-based vector at MOI 0.1. Simultaneously, the cells were treated with tested compounds. Luciferase expression was assayed 24 h after transduction. Data were normalized to the luciferase expression level in DMSO-treated samples. Mean values ± SD (n = 3) are shown. (G) Cell viability (24 h) of 293T, Jurkat, and CEM in the presence of s17 measured with MTT assay. Mean values ± SD (n = 3) are shown. (H) The effect of s17 on 293T, Jurkat, and CEM transduction with HIV_wt vector. Data were normalized to the luciferase expression level in DMSO-treated samples. Mean values ± SD (n = 3) are shown.