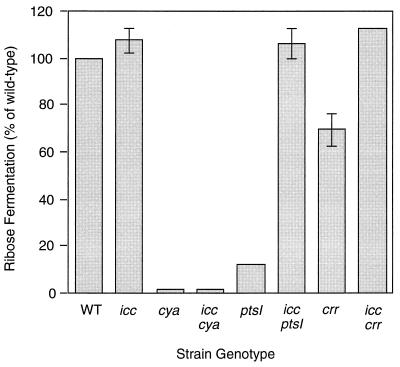
FIG. 3.
Effect of icc disruption on ribose fermentation in wild-type (WT), cya, and PTS-disrupted backgrounds. A 100-μl aliquot of exponentially growing wild-type or mutant strains was inoculated into 5 ml of supplemented PRB plus 1% ribose. After rotation of the cultures overnight, we measured the pH of each culture and calculated the pH change (ΔpH). The degree of ribose fermentation of each mutants strain was expressed as a percentage of wild-type ΔpH (wild-type H. influenzae cultures in 1% ribose showed an average pH drop from 7.47 to 5.43). Mean values from three replicates are shown. Error bars represent SEM. (SEM values for cya, icc cya, ptsI, and icc crr strains are too small to be visible on this scale.)