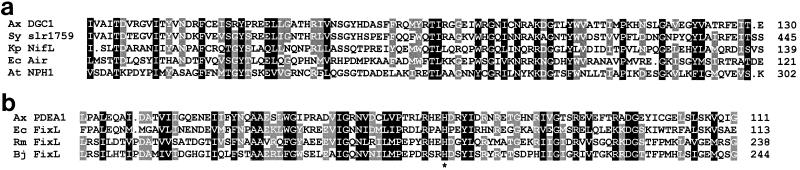
FIG. 5.
Multiple alignment of the N-terminal regions of the DGC1 and PDEA1 sequences showing conservation with domains on other proteins. Residues with identity or conservative substitution in 100 and ≥75% of the sequences are shaded in black and gray, respectively. (a) The amino acid sequences shown are from A. xylinum (Ax) DGC1, Synechocystis strain PCC6803 (Sy) slr1759 (sensory transduction histidine kinase, GenBank accession no. D90903), Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp) NifL (GenBank X13303), E. coli (Ec) Aer (GenBank U28379), and Arabidopsis thaliana (At) NPH1 (GenBank AF030864). (b) Amino acid sequences shown are A. xylinum (Ax) PDEA1, E. coli (Ec) FixL (GenBank D90790), Rhizobium meliloti (Rm) FixL (GenBank Z70305), and Bradyrhizobium japonicum (Bj) FixL (GenBank P23222). An asterisk indicates a His residue conserved among FixL and PDEA proteins.