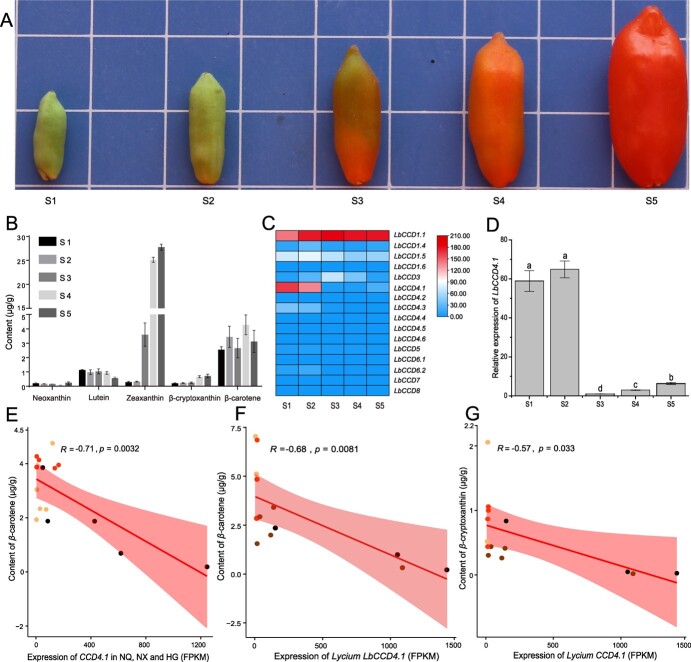
Figure 1.
LbCCD4.1 was associated with the carotenoid content. A Appearance of Lycium barbarum’s fruit at five key developmental stages (S1–S5). B Dynamics of carotenoid metabolites in NQ fruit during five key developmental stages, and the histograms of every metabolite from left to right indicated S1, S2, S3, S4, and S5, respectively. C Heatmap of quantitative expression dynamics of LbCCD family genes in NQ fruit at the five key developmental stages based on transcriptome sequencing. D Relative expression of LbCCD4.1 in NQ fruit during the five key developmental stages. E Correlations between the β-carotene content and CCD4.1 expression among NQ (red dot), NX (yellow dot), and HG (black dot) fruits during stage S1 to S5. F and G Correlations between the β-cryptoxanthin content, β-carotene content, and CCD4.1 expression among 14 Lycium accessions. The 14 Lycium included four NQ (red dot), two NX (yellow dot), three HG (black dot), and five other types (brown dot). The expression and metabolite content measurements included three biological replicates, and values are presented as averages ± standard deviations. Multiple comparisons were performed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).