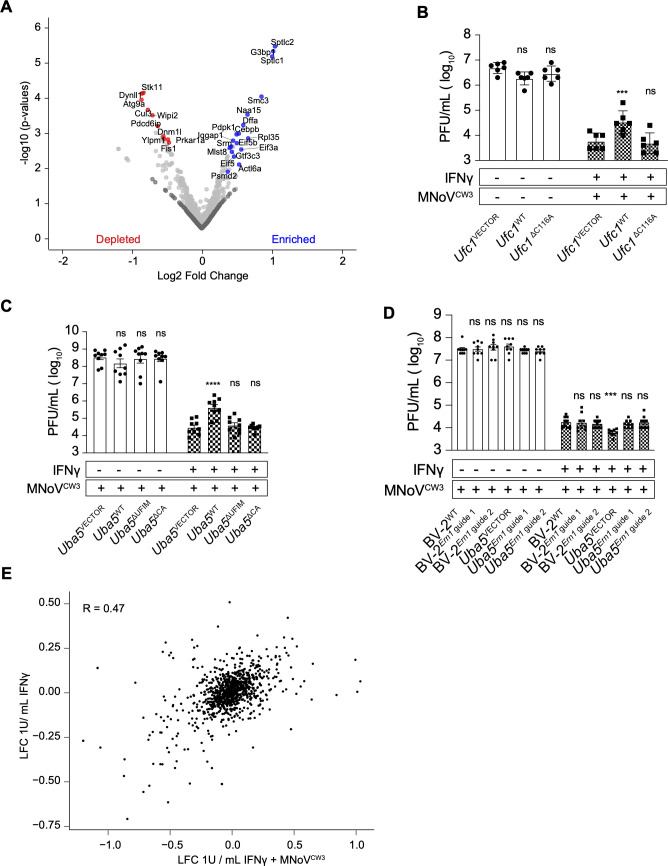
Fig 3.
Identification of genes required for IFNγ-induced norovirus cytopathicity in BV-2 cells. (A) Volcano plot of guides enriched or depleted after 1 U/mL IFNγ + norovirus infection relative to mock treatment. (B) Plaque assay of Ufc1VECTOR, Ufc1WT, and Ufc1ΔC116A BV-2 cells as described in Fig. S1. (C) Plaque assay of Uba5VECTOR, Uba5WT, Uba5ΔUFIM, and Uba5ΔCA BV-2 cells as described in Fig. S1. (D) Plaque assay of BV-2WT, BV-2Ern1 guide 1, BV-2Ern1 guide 2, Uba5VECTOR, Uba5Ern1 guide 1, and Uba5Ern1 guide 2 cells as described in Fig. S1. (E) Average LFC of 1 U/mL IFNγ condition versus LFC of 1 U/mL IFNγ + norovirus condition. For volcano plots, the average log2 fold change (LFC) of all sgRNAs for each gene is plotted against the −log10(P value) for each gene. Blue and red highlighted genes in (A) represent a STARS score with FDR < 0.01, and dark gray genes represent non-targeting guides. Values in (B–D) represent means ± SEM from 2 to 3 independent experiments. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 and ****P ≤ 0.0001 were considered statistically significant. ns, not significant. P value was determined by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.