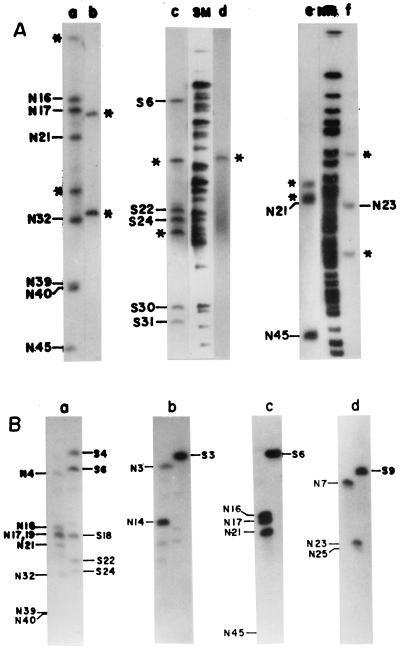
FIG. 3.
(A) Identification of NotI or SfiI fragments of the V. cholerae SG24 genome in isolated CeuI fragments. CeuI fragments C3 (lanes a and c) and C6 (lanes b and d) were completely digested with NotI or SfiI, end labeled, and separated by PFGE. Identification of NotI fragments in isolated SfiI fragments. SfiI fragments S6 (lane e) and S9 (lane f) were completely digested with the enzyme NotI, end labeled, and separated by PFGE. NotI (NM)- or SfiI (SM)-digested, end-labeled SG24 genomic DNA was used as a marker for identification of linked fragments. Asterisks denote the flanking DNA fragments. (B) Assignment of the flanking NotI or SfiI fragments (shown in panel A) of V. cholerae SG24 genomic DNA in isolated CeuI fragments. Radiolabeled CeuI fragment C3 (a) or C6 (b) was used as the probe for Southern hybridization with the NotI- or SfiI-digested genome of V. cholerae SG24. For identification of the flanking NotI fragments in isolated SfiI fragments of the genomic DNA of strain SG24, radiolabeled SfiI fragment S6 (c) or S9 (d) was used as the probe for Southern hybridization with the NotI- or SfiI-digested SG24 genome. Hybridizations were carried out at 60°C. The filters were washed under stringent conditions as described in Materials and Methods.