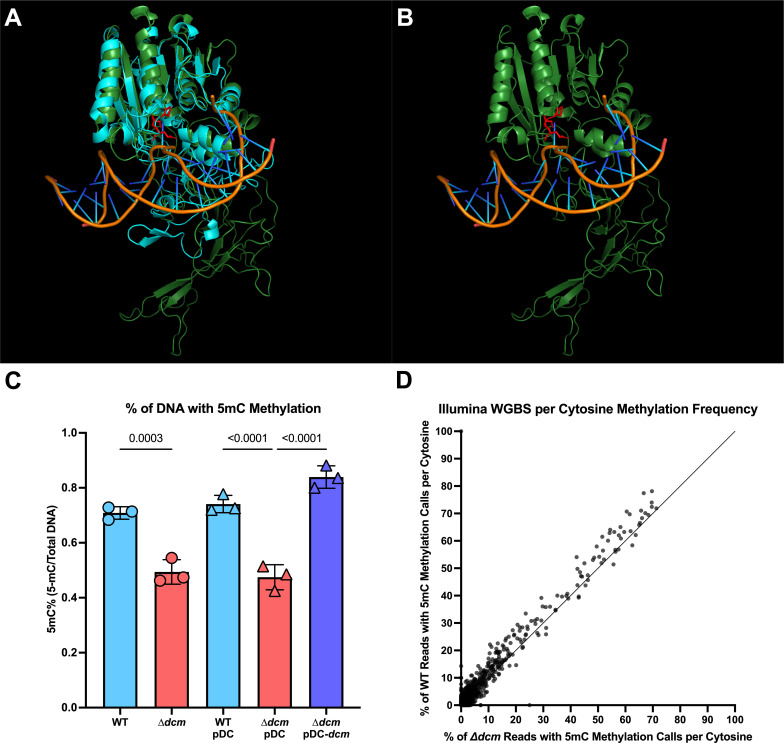
Fig 2.
Dcm DNA binding structure and 5mC methylation are conserved. (A and B) Alphafold2 (21) was used to generate a predictive model of the GBS Dcm based on the crystal structure of Haemophilus influenzae HaeIII Dcm bound to DNA (22). (A) Structural alignment of the GBS Dcm predicted structure (green) and the crystal structure of HaeIII (cyan) is displayed by using PyMOL (24). (B) CJB111 Dcm with DNA from the HaeIII crystal structure overlayed to display predicted DNA binding. The conserved PCQ motif required for 5mC methylation (25) is shown in red. (C) Percentage of total DNA with 5mC methylation from WT, ∆dcm, WT + pDC, ∆dcm + pDC, and ∆dcm +pDC dcm is shown as measured by ELISA. Each dot represents the mean of three technical replicates in an independent experiment, bars represent the average of these dots, and the error bars represent the SEM. (D) Enzymatic methyl-seq was used to convert non-5mC methylated cytosines to uracils for Illumina whole genome bisulfite sequencing. Bismark was used to identify 5mC methylation. The percentage of reads with a positive methylation call at each cytosine position from WT GBS genomic DNA is graphed against the percentage of reads with a positive methylation call at the same cytosine position in ∆dcm GBS genomic DNA.