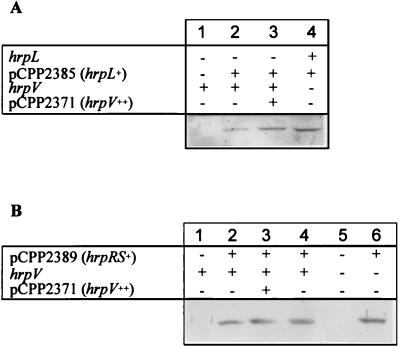
FIG. 4.
Prevention of hrpV-dependent inhibition of HrcJ accumulation by constitutive expression of hrpL and hrpRS. All bacteria were grown in LM medium and assayed for the accumulation of HrcJ by immunoblot analysis, as described in the legend to Fig. 1, but with chromogenic immunodetection. Cultures denoted hrpL− carried a chromosomal hrpL::TnphoA mutation; those denoted hrpV− carried a ΔhrpV::nptII mutation. (A) Lanes: 1, P. syringae pv. syringae 61–2074; 2, P. syringae pv. syringae 61–2074(pCPP2385); 3, P. syringae pv. syringae 61–2074(pCPP2385/pCPP2371); 4, P. syringae pv. syringae 61–N407(pCPP2385). (B) Lanes: 1, P. syringae pv. syringae 61; 2, P. syringae pv. syringae 61(pCPP2389); 3, P. syringae pv. syringae 61(pCPP2389/pCPP2371); 4, P. syringae pv. syringae 61(pCPP2389/pML122); 5, P. syringae pv. syringae 61–N407; 6, P. syringae pv. syringae 61–N407(pCPP2389).