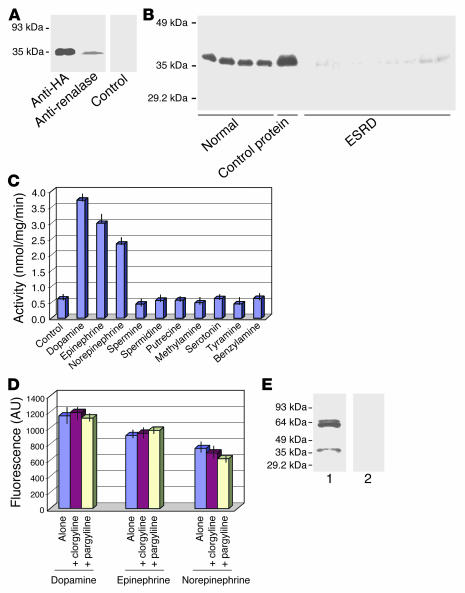
Figure 2.
Renalase is a secreted amine oxidase. (A) Detection of renalase in culture medium of HEK293 cells transiently transfected with renalase cDNA. Control, secondary antibody alone. (B) Western blot analysis of human plasma using an anti-renalase antibody. Normal, plasma from individuals with normal renal function; Control protein, human recombinant renalase protein; ESRD, plasma from patients with ESRD receiving hemodialysis. (C) Renalase metabolizes catecholamines. Ten micrograms of GST-renalase fusion protein was used for each assay; amine oxidase is expressed as H2O2 production (nmol/mg/min). (D) Renalase activity is insensitive to known monoamine oxidase inhibitors. The renalase activity was assessed as described in C, with dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine as substrates. The renalase activity was examined in the absence of inhibitor (Alone), in the presence of 1 μM clorgyline, or in the presence of 1 μM pargyline. Renalase activity is expressed as arbitrary fluorescence units/10 μg protein. In control studies, clorgyline (1 μM) and pargyline (1 μM) inhibited MAO-A activity by 83.9% ± 2.3% (n = 3) and 82.4% ± 1.9% (n = 3), respectively. (E) Affinity purification of human renalase. The anti-renalase polyclonal antibody was used to isolate protein from human urine. Lane 1: renalase from human urine; lane 2: control with secondary antibody alone.