FIGURE 1.
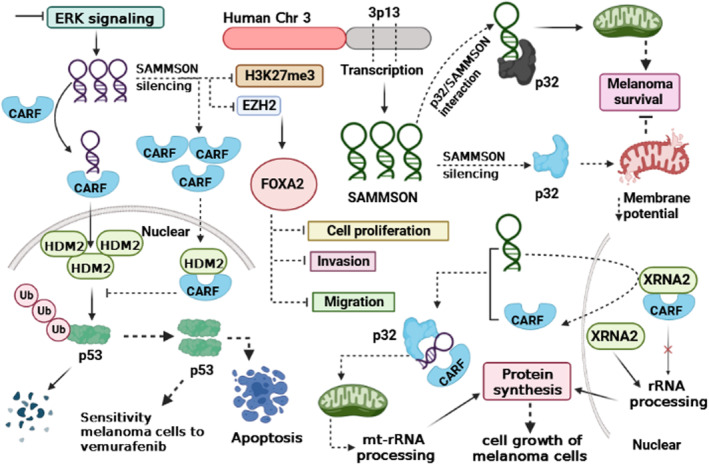
SAMMSON via different mechanisms exerts its oncogenic roles in melanoma. SAMMSON promotes melanoma progression by affecting different signalling pathways, mitochondria biogenesis, protein synthesis, cell proliferation, invasion and migration. The overexpression of SAMMSON inhibits the localisation of CARF to nucleus which leads ubiquitination of p53 by HDM2 and follows its degradation. After silencing SAMMSON, CARF can translocate to the nucleus and interacts with HDM2, which inhibits ubiquitination of p53. On the contrary, silencing of SAMMSON increases FOXA2 expression that inhibits tumour progression. SAMMSON via interaction with CARF and p32 plays a pivotal role in the processing of mt‐rRNA and protein synthesis. Ub: Ubiquitin, CARF: Collaborator of Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma, HDM2 (or MDM2): Is an E3 ubiquitin‐protein ligase, EZH2: Enhancer of zeste homologue 2, H3K27me3: Trimethylation of lysine 27 in histone H3, FOXA2: Forkhead box protein A2, XRN2: 5′‐3′ exoribonuclease 2, Mt: Mitochondria, Chr: Chromosome.
