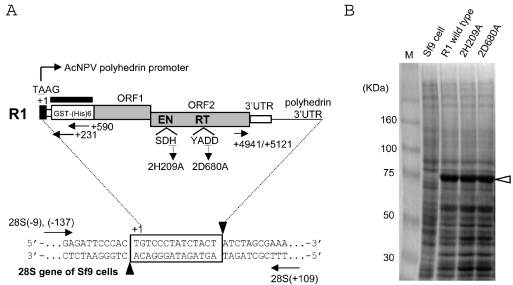
Figure 2.
In vivo retrotransposition assay for R1 elements using recombinant baculoviruses. (A) Diagram of the PCR assay for retrotransposition. Shown at the top of the figure is a diagram of the R1 element expressed from AcNPV. The 5′UTR sequence derived from the polyhedrin promoter and ORF1/ORF2 of R1 are shaded in black and gray, respectively. Nucleotide position is numbered with the transcription initiation site (A of TAAG) defined as +1. EN and RT denote the endonuclease and reverse transcriptase domains, respectively. The amino acid position of each mis-sense mutant is also shown; the 2H209A mutant represents the substitution of the 209th histidine (H) in the ORF2 for alanine (A), and the 2D680A mutant represents the substitution of the 680th aspartic acid (D) in the ORF2 for alanine (A). Shown at the bottom is a diagram of an rDNA unit showing the location of R1 insertion; 14 bp of the target site duplication (TSD) created upon R1 insertion is boxed. The putative cleavage sites by R1-EN are indicated by black arrowheads. Arrows represent the primer set to amplify the 5′ and 3′ junctions between the R1 sequence and the 28S sequence. The thick bar above the GST region which is fused to the R1 ORF1 indicates the probe used for Southern hybridization in Figure 4. (B) Expression of R1 proteins with a baculovirus-based expression system. The total proteins were extracted from Sf9 cells infected with recombinant viruses shown above and run on SDS–PAGE; the predicted molecular weight for R1 GST/(His)6/ORF1 was 78 170. Lane M; size markers.