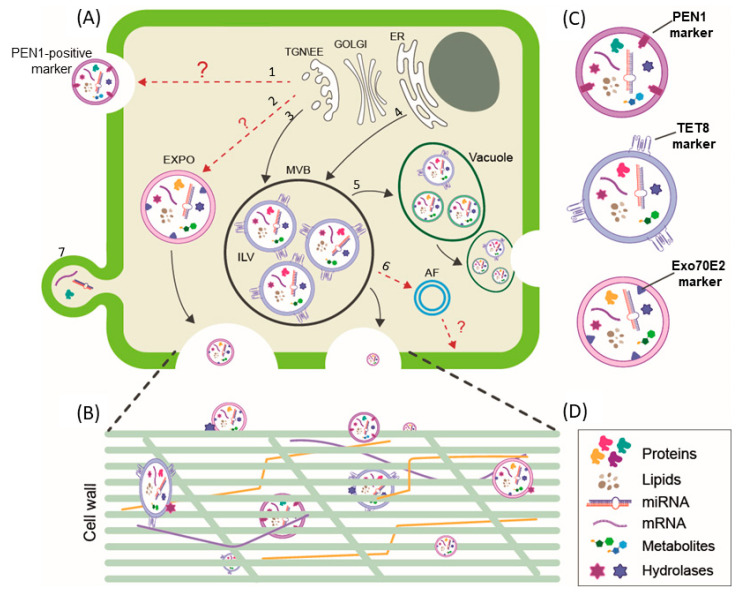
Figure 2.
Plant EV biogenesis and release. (A) Possible EV biogenesis pathways in plants. Plant EVs might be derived from PEN1-positive organelles (1); exocyst-positive organelles (EXPOs) (2); multivesicular body (MVB) endosomes (3); ER-derived vesicles (4); vacuole fusion with the plasma membrane (5); autophagosome-mediated secretion (6); or blebbing of the cell membrane (7). (B) Passage of EVs through the plant cell wall might involve cell wall hydrolases. Cell wall as well as EV plasticity could further facilitate their cell wall crossing. (C) Schematic representation of biomarker-associated EVs. (D) Plant EV composition. TGN/EE: trans-Golgi network/early endosome; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; EXPO: exocyst-positive organelle; MVB: multivesicular body; ILV: intraluminal vesicle; AF: autophagosome. ? means putative route.