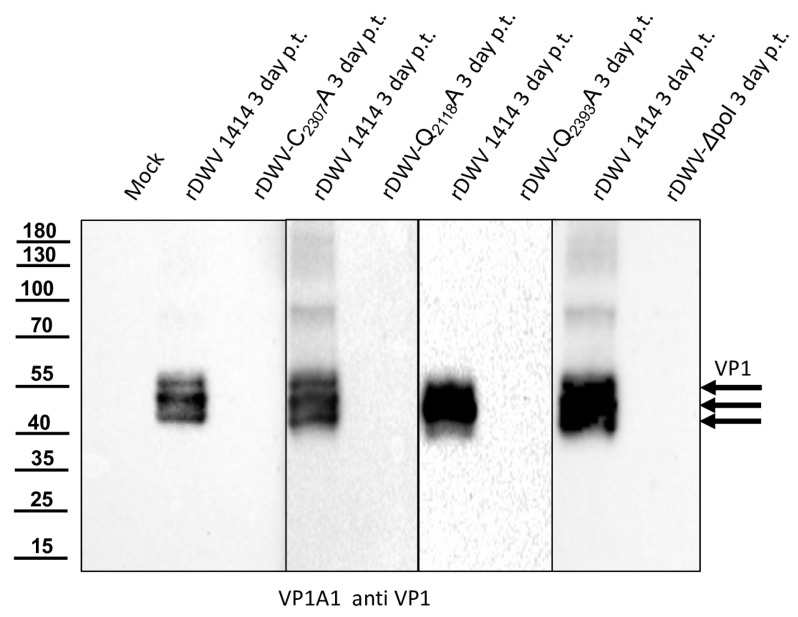
Figure 13.
Western blot analysis of 3CL protease and cleavage site mutants. Honey bee pupae were transfected with synthetic RNA of DWV strain 1414 (rDWV 1414), a mutant genome of DWV with an exchange of the active cysteine (rDWV-C2307A), a mutant genome with an exchange of the 3BCL cleavage site (rDWV-Q2118A), a mutant genome with an exchange of the 3CDL cleavage site (rDWV-Q2393A), and a mutant genome with a deletion of the complete 3DL (rDWV-Δpol). DWV RNA transfected and mock-transfected control pupae were harvested three days post-transfection (p. t.). The pupae were homogenized and total bee protein was resolved via SDS-PAGE. A Western blot analysis of the honey bees using anti-VP1 Mab VP1A1 showed no signal in the mock-transfected pupa, and no signals in the bee pupae transfected with DWV genomes with mutations of the active cysteine, the N-terminal, and the C-terminal cleavage site of 3CL protease or with a deletion of the complete RdRp gene. In contrast, a typical VP1 pattern with bands at 47, 42, and 39 kDa appeared in all wild-type DWV RNA-transfected pupa indicating successful transfection, infection, and virus growth. Because the transfections and mutation analyses were performed at different time points and analyzed on different Western blots, the signals from the wild-type control infections are included side by side for each analysis to control RNA synthesis, transfection and VP1 signal intensity, respectively.