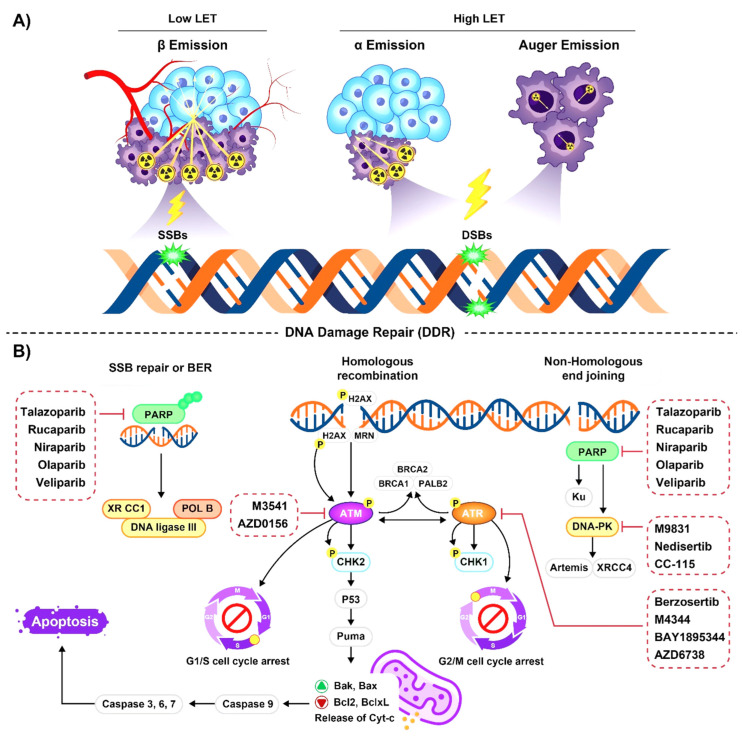
Figure 2.
(A) Visualization of DNA damage induction patterns of beta-emitters, alpha-emitters, and auger electron emitters exhibits distinct patterns of DNA damage induction based on their penetration range and complexity of DNA damage. Beta-emitters induce isolated lesions over a longer range, alpha-emitters induce more complex damage in a localized area, and auger electrons generate high-density damage in close proximity to the DNA molecule. (B) The general overview of DNA damage repair (DDR) pathway initiation by sensor proteins that detect DNA damage, followed by activation of transducer proteins and subsequent phosphorylation of effector proteins. The activation of cell cycle checkpoints and recruitment of DNA repair factors are key components of the DDR, ensuring accurate repair of DNA lesions and maintenance of genomic stability. The DDR inhibitors are shown in red boxes. ATM: ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, ATR: ataxia-telangiectasia rad3-related protein, DNAPKs: DNA-dependent protein kinase, PARP: poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase, CHK1/2: checkpoint kinase1/2, Bax: B cell lymphoma-associated X, Bcl-2: B cell lymphoma-2, Cyt-c: cytochrome c, BER: base excision repair, SSB: single-strand break, DSB: double-strand break, LET: linear energy transfer.