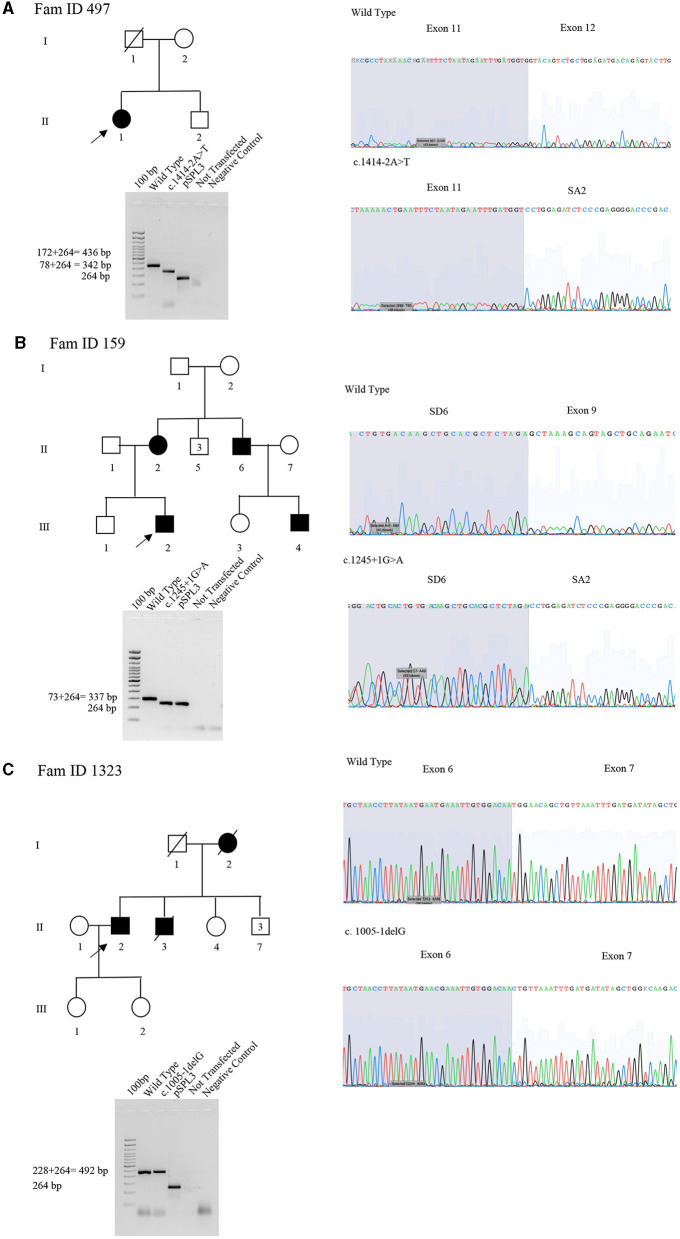
Figure 2.
Pedigree, minigene assay, Sanger sequencing of SPAST families 497, 159, and 1,323. (A) Family ID 497. Agarose gel shows RT-PCR results of minigene assay for variant c.1414-2A>T. In lane 1 is shown an amplicon of 436 bp correspondent to a wild-type genotype (172 bp of normal splicing of exons 11 and 12 + 264 bp of pSPL3 exon); in lane 2 is shown an amplicon of 358 bp correspondent to abnormal splicing produced by variant c.1414-2A>T (358 bp [80 bp of normal splicing (exon 11)−92 bp of exon 12 loss] + 264 bp of pSPL3 exon); in lane 3 is shown the amplification of pSPL3 without SPAST cloning; in lane 4 is shown the amplification of HEK 293 T cDNA without transfection of pSPL3; and in lane 5 is shown negative control of PCR amplification. Sanger sequence shows the loss of exon 11 and normal sequence. (B) Family ID 159. Agarose gel shows RT-PCR results of minigene assay for variant c.1245+1G>A. In lane 1 is shown an amplicon of 337 bp correspondent to a wild-type genotype (74 bp of normal splicing of exon 9 + 264 bp of pSPL3 exon); in lane 2 is shown an amplicon of 264 bp correspondent to abnormal splicing produced by variant c.1245+1G>A (264 bp [74 bp of normal splicing (exon 9) – 74 bp (exon 9)] + 264 bp of pSPL3 exon); in lane 3 is shown the amplification of pSPL3 without SPAST cloning; in lane 4 is shown the amplification of HEK 293 T cDNA without transfection of pSPL3; and in lane 5 is shown negative control of PCR amplification. Sanger sequence shows the loss of exon 9 in SPAST gene and normal sequence. (C) Family ID 1323. Agarose gel shows RT-PCR results of minigene assay for variant c.1005-1delG. In lane 1 is shown an amplicon of 492 bp correspondent to a wild-type genotype (228 bp of normal splicing of exons 6 and 7 + 264 bp of pSPL3 exon); in lane 2 is shown an amplicon apparently of 492 bp correspondent to normal splicing produced by variant c.1005-1delG (492 bp [134 bp of normal splicing (exons 6) – 94 bp (exon 7)] + 264 bp of pSPL3 exon); in lane 3 is shown the amplification of pSPL3 without SPAST cloning; in lane 4 is shown the amplification of HEK 293 T cDNA without transfection of pSPL3; in lane 5 is shown negative control of PCR amplification. Sanger sequence shows the loss of eight nucleotides of exon 7 causing the loss of frame and a premature stop codon.