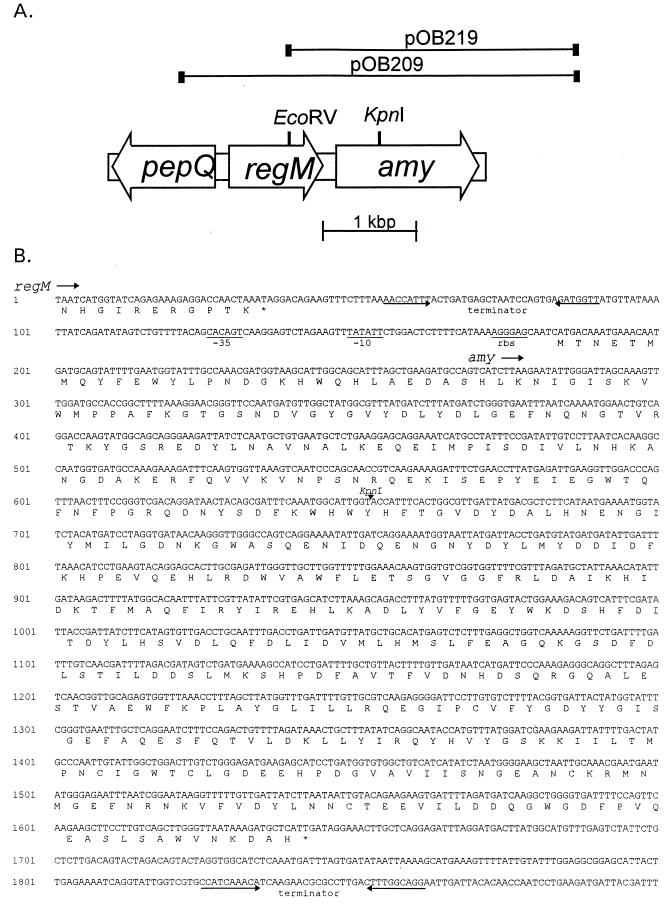
FIG. 1.
Sequence analysis of the amy locus. (A) Genetic organization of the amy region in S. mutans. Clones expressing amylase activity are shown, with the EcoRV site used for producing subclone pOB219 and the KpnI site used to inactivate the amy gene by insertion of a kanamycin resistance cassette. (B) Nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of the amy region from the end of regM. Potential ribosome binding sites (rbs), −10 and −35 promoter elements, and terminators are indicated. The KpnI site used to inactivate the amy gene by insertion of a kanamycin resistance cassette is indicated.