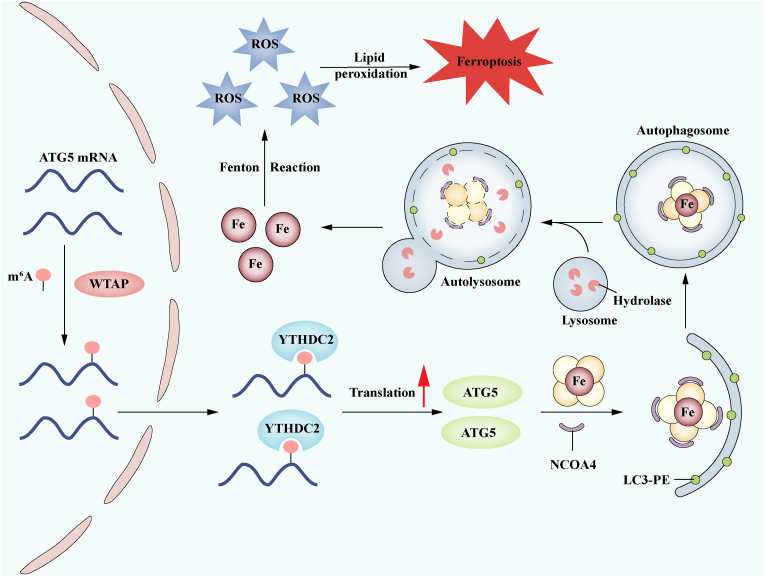
Fig. 7.
WTAP-mediated m6A modification on ATG5 mRNA is dependent on YTHDC2 in autophagic iron death in HCC. Following the administration of HCC ferroptosis inducers, they triggered WTAP-mediated m6A modification on ATG5 mRNA, which was then recognized and bound by YTHDC2. This resulted in enhanced translation and elevated expression of ATG5, which then started ferritinophagy, an increase in the unstable iron pool, and eventually led to the onset of ferroptosis in HCC.