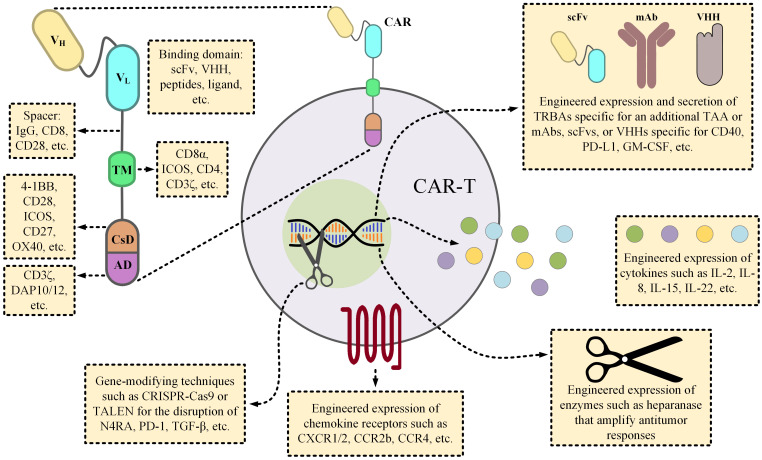
Figure 4.
The details of a CAR molecule and the various strategic twists proposed by scientists to overcome the obstacles of CAR-T therapies. From the early days of CAR-T development, various components have been incorporated into CAR constructs. Since such components could substantially influence the functionality of the CAR-Ts, their selection has been a subject of paramount importance. For instance, the length of the spacer fragment can influence the cytokine production profile of the CAR-Ts, or the choice of the co-stimulatory domain(s) can have substantial impacts on the expansion, persistence, or even the phenotypic features of the CAR-Ts. Researchers have engineered CAR-Ts to secrete TRBAs (for example against a different TAA, rather than the one targeted by CAR-Ts, to augment antitumor responses) or other forms of mAbs for neutralizing the mediators of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) or to counteract immunosuppression. CAR-Ts can also be manipulated to produce factors, such as ILs, that boost their effector function, or to express enzymes that help modify the components of the tumor microenvironment for facilitating intratumoral trafficking of the immune effector cells. In regard to increasing CAR-T accumulation in tumor sites, investigators have also engineered CAR-Ts to express the cognate receptors of the molecules that are overexpressed by tumor cells, and they have reported encouraging results (27, 28). Ultimately, CAR-T therapies can also benefit from the novel gene-modifying techniques in a way that they can be utilized for the generation of immunosuppression-resistant or off-the-shelf CAR-Ts through the disruption of immunosuppressive genes or TCR αβ chains, respectively. AD, activation domain; CsD, costimulatory domain; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ICOS, inducible T-cell costimulator; IL, interleukin; mAb, monoclonal antibody; scFv, single-chain variable fragment; TAA, tumor-associated antigen; TALEN, transcription activator-like effector nucleases; TCR, T-cell receptor; TM, transmembrane domain; TRBA, T-cell-redirecting bispecific antibodies.