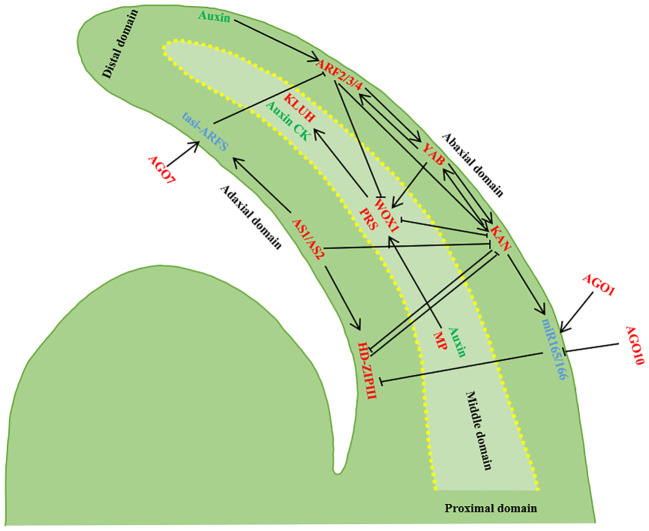
Figure 2.
Establishment of leaf polarity. The developing leaf primordium has three domains, and the transcription factors in the three domains inhibit each other’s expression and control each other. Transcripts of AS1/AS2, HD-ZIPIII and tasi-ARF accumulate in the adaxial domain of the leaf primordium, transcripts of ARF 3/ARF4, KAN and miR165/166 accumulate in the abaxia domain, and WOX1/PRS are expressed in the intermediate domain of the leaf primordium. AGO10 inhibits miR165/166, AGO1 regulates miR165/166 and miR165/166 inhibits HD-ZIPIII. AGO7 stabilizes ta-siR-ARF, and ta-siR-ARF degrades of ARF2/3/4. tasi-ARF and miR165/166 Rnas can move between cells and inhibit ARF2/3/4 and HD-ZIPIII after transcription, and ARF2/3/4 is controlled by auxin. KAN and HD-ZIPIII antagonized each other, and ARF2/3/4 and KAN were inhibited by AS1/AS2. KAN inhibited the expression of WOX1 and PRS, while WOX1 and PRS inhibited the expression of KAN. Adaxial expression of MP and off-axes enrichment of auxin together localized WOX1 and PRS expression in the intermediate domain. In addition, MP may be the direct target of positively expressed HD-ZIPIII, and YAB promotes the expression of WOX1/PRS with KAN and ARF2/3/4, while YAB promotes the expression of WOX1/PRS (Barkoulas et al., 2007; Kalve et al., 2014; Du et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2021a).