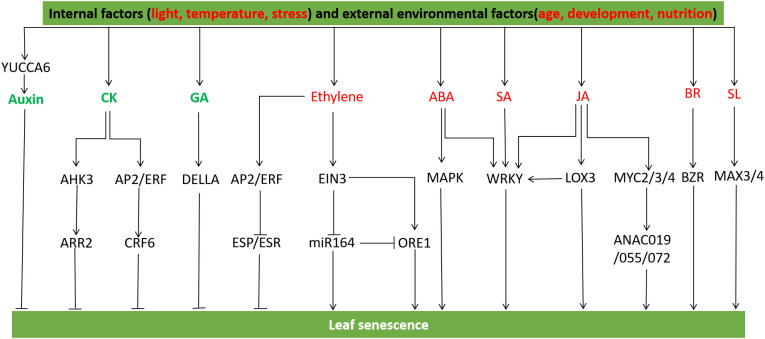
Figure 5.
Hormonal and gene regulation of leaf senescence. YCCA6 regulates auxin biosynthesis and inhibits leaf senescence. The AP2/ERF transcription factor CRF6 mediated by cytokinin inhibits senescence, and the cytokinin receptor AHK3 regulates leaf senescence through the regulatory factor ARR2. The abnormal accumulation of DELLA protein delayed leaf senescence by blocking GA biosynthesis. Ethylene activated AP2/ERF gene to regulate leaf senescence, ERF transcription factor inhibited the expression of ESP/ESR, a negative regulator of leaf senescence, ESR knockout promoted leaf senescence, while ESR overexpression did the opposite. EIN3 activates ORE1 and NAP to positively regulate leaf senescence. EIN3 inhibits miR164 transcription and up-regulates the transcription level of ORE1/NAC2, the target gene of miR164. ABA induces WRKY transcription factor and promotes early senescence of leaves under dark treatment. SA treatment induces SAGs expression, and WRKY influences plant aging and defense signaling pathways in SA-mediated signaling cascades. WRKY interacts with JA biosynthesis gene LOX3 to promote leaf senescence, MYC2/3/4 protein can activate JA-induced chlorophyll degradation, and the signaling pathway of MYC2/3/4 and NAC protein ANAC019/055/072 induces leaf senescence. BRs activates BZR family transcription factors to promote leaf senescence. SL genes MAX3 and MAX4 accelerate leaf senescence (Mayta et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2021a).