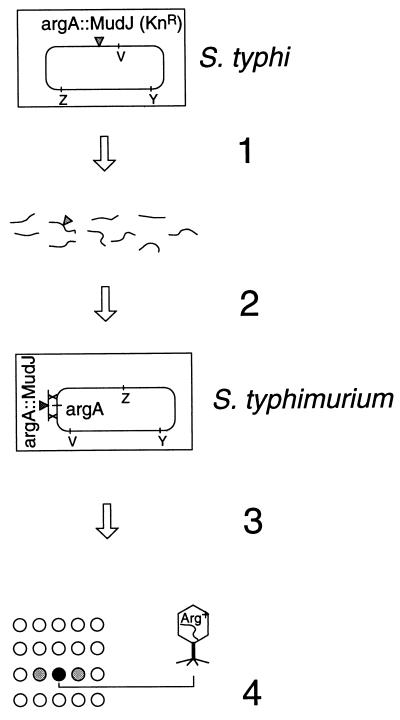
FIG. 1.
Outline of mapping procedure. Step 1. Chromosomal DNA from an S. typhi strain carrying the MudJ insertion to be mapped (for example, the argA locus) is extracted and mildly sheared. Step 2. DNA is used to electrotransform an S. typhimurium recipient in which the recD and mutS genes are inactivated. Selection for Kanr yields recombinants in which the argA locus on the recipient chromosome has been replaced by the argA::MudJ marker. (Although the chromosomal region containing argA is inverted in S. typhimurium relative to S. typhi, the gene order within this region is conserved between the two bacteria.) Step 3. Recombinant bacteria are spread on a minimal plate, and phage P22 transducing lysates individually enriched for various portions of the S. typhimurium chromosome are spotted on the bacterial lawn. Step 4. The lysate enriched for the region carrying the wild-type allele of the MudJ-disrupted locus gives rise to prototrophic transductants (patch of colonies in the spotted area).