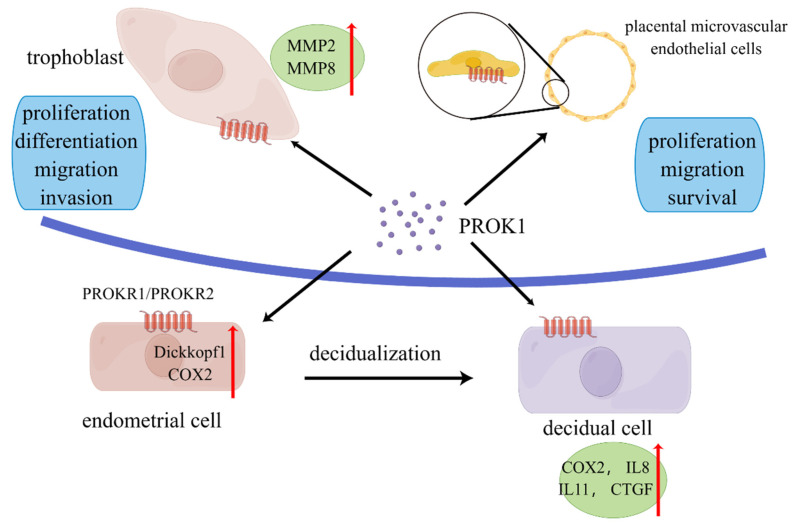
Figure 1.
Role of prokineticin1 in the maternal-fetal interface. PROK is secreted mainly by placenta. PROK1 can promote proliferation, differentiation, migration and invasion of trophoblasts through upregulation of MMPs and other pathways. PROK1 acts on placental microvascular endothelium and affects angiogenesis. It acts on endothelial stromal cells and affects decidualization through upregulation of COX2, dickkopf1, etc. PROK1 affects placental implantation through regulation of IL8, IL11 and other cytokines. By Figdraw (www.figdraw.com).