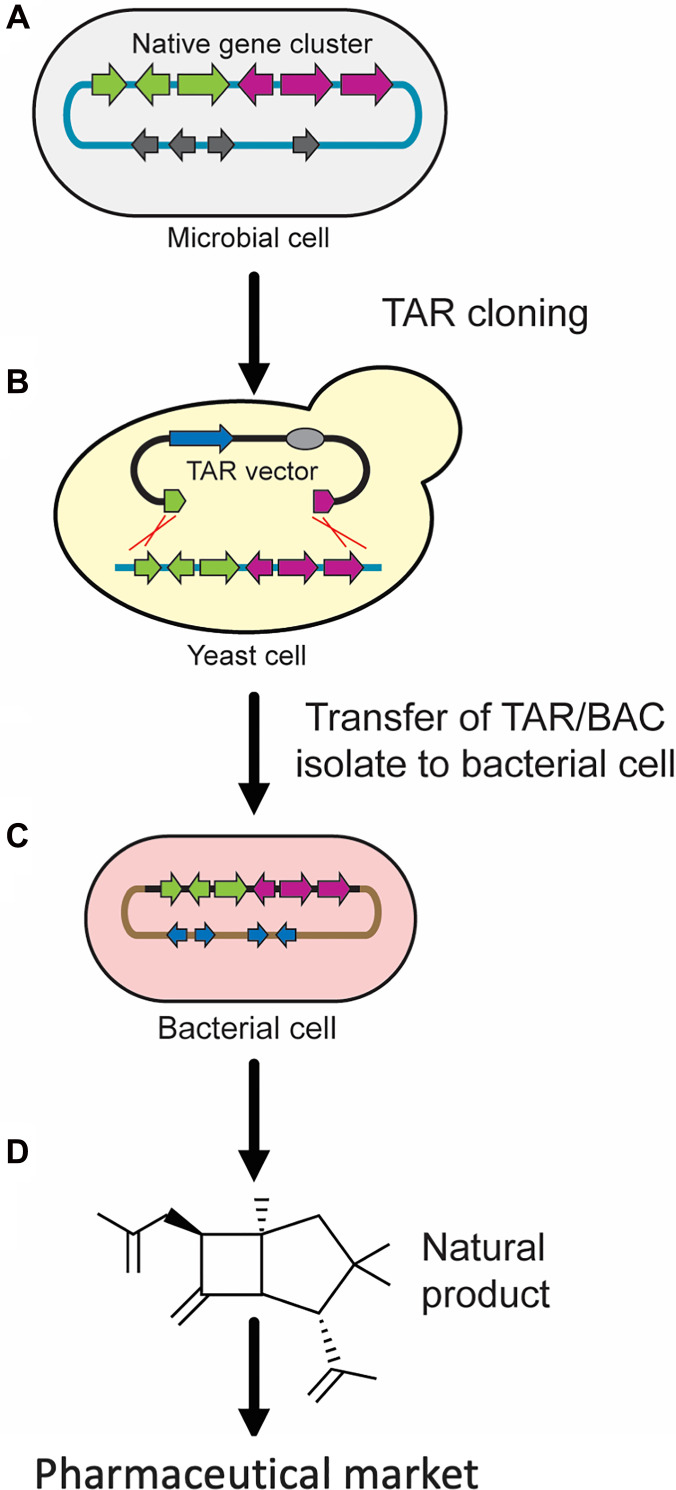
Figure 8. TAR cloning of natural product biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) from microbial genomes.
(A) Organization of a native gene cluster located on a chromosome propagated in a microbial cell. (B) Isolation of BGC by TAR vector where the hooks (in green and in purple) correspond to the ends of the gene cluster. TAR is based on homologous recombination between the hooks of TAR vector and co-transformed genomic DNA isolated from host microbial cells that leads to formation of a circular YAC/BAC construct. In the TAR vector, the hooks or homology arms (in green and in purple) correspond to the ends of the cluster. (C, D) TAR-cloned gene cluster is transferred to bacterial cells and, if necessary, integrated into the chromosome of a host strain for basic research or production of natural compounds.