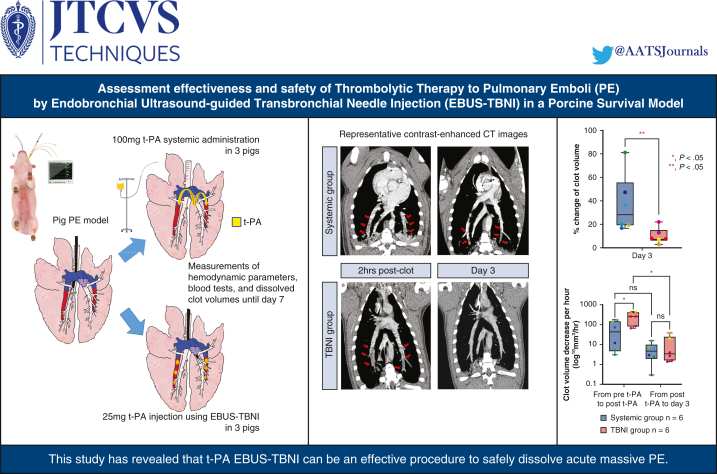
Figure 6.
Summary of this study on the safety and effectiveness of endobronchial ultrasound–guided transbronchial needle injection (EBUS-TBNI) in a porcine survival model. A pig model of pulmonary embolism (PE) was created by injecting clots into the pulmonary artery of healthy pigs under EBUS guidance. One group received 100 mg of t-PA systemic administration to treat PE (systemic group); the other group received each 25 mg of t-PA injection into bilateral PEs using EBUS-TBNI (total of 50 mg t-PA). Hemodynamic parameters, blood tests, and CT scans were collected to evaluate the clot dissolving. In TBNI group, the speed of dissolving clot was significantly greater than in the systemic group. There were no complications in both groups. Twenty-five milligrams of t-PA injection using EBUS-TBNI can be a safe and effective procedure to treat acute massive PE. The promising efficacy data suggest a potential role for clinical practice. t-PA, Tissue plasminogen activator; CT, computed tomography.