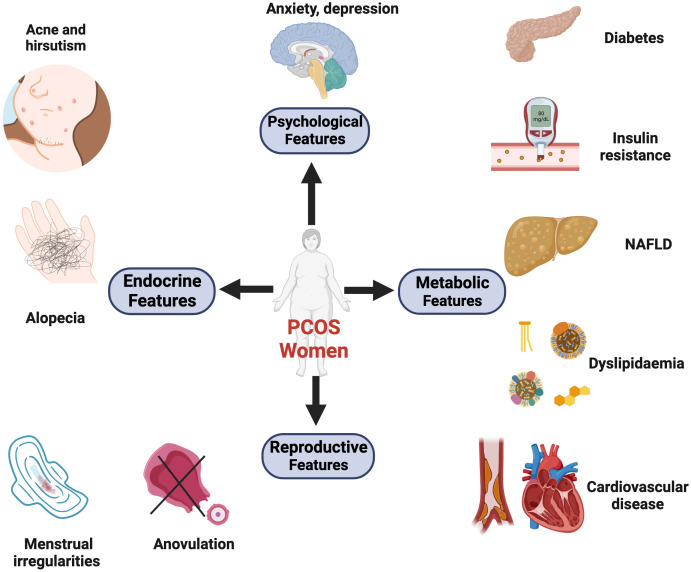
Figure 1.
The major clinical manifestations of PCOS. These symptoms can be divided into four categories: reproductive, endocrine, metabolic, and psychological comorbidities. (1) Reproductive features: the dysregulated hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis and neuroendocrine factors contribute to menstrual irregularities, anovulation, infertility, and increased risks of pregnancy complications. (2) Endocrine features: hormonal imbalances (ovarian and adrenal hyperandrogenemia). Symptoms like hirsutism, acne, and androgenic alopecia are induced by high levels of circulating androgens. (3) Metabolic features: 30% of lean and 70% of obese patients exhibit insulin resistance. Additionally, women with PCOS suffer from abdominal obesity, dyslipidemia, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). These metabolic abnormalities can result in long-term cardiometabolic sequelae, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and atherosclerotic disease. (4) Psychological features: PCOS is associated with an increased prevalence of depression, anxiety, and poor quality of life. Created with BioRender.com.