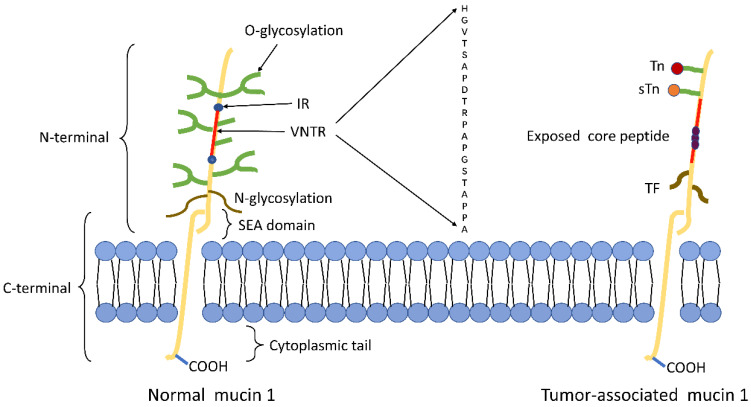
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of MUC1 structure. (A) The structure of MUC1 in normal tissues. MUC1-N contains the signal peptide, VNTR region (red), and SEA domain. The VNTR region of MUC1-N is composed of 20 amino acids that are extensively O-glycosylated (green) at the serine and threonine residues. The VNTR region is flanked by IR (blue) sequences. MUC1-N and MUC1-C are sparingly N-glycosylated (brown) at asparagine residues. MUC1-C consists of the SEA, the transmembrane domain and the MUC1-CD. (B) The structure of MUC1 in tumor tissues. The abnormal glycosylation of the tumor-associated MUC1 leads to the formation of new carbohydrate side chains [Tn (red), sTn (orange), TF (black)] and the exposure of core peptide(black).