Figure 1.
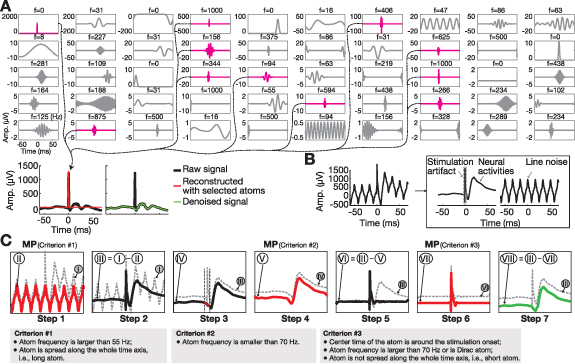
Schematic overview of matching pursuit-based artifact reconstruction and removal method (MPARRM). (A) The matching pursuit (MP) algorithm iteratively decomposes a signal into a linear combination of basis functions (i.e. atoms). In a simplified denoising procedure, the raw signal (black) containing a strong individual stimulation artifact around time 0 is decomposed into 50 atoms using the MP algorithm (Chandran KS et al 2016). Selecting atoms representing stimulation artifacts (magenta) and reconstructed individual stimulation artifact (red). Removing the reconstructed stimulation artifact from the raw signal yields a denoised signal (green). (B) Brain signals recorded during electrical stimulation are comprised of three major components, including electrical line noise, sharp stimulation artifact, and neural activity (i.e. rhythmic and transient electrophysiological signals). (C) Description of MPARRM. Dashed grey trace (Roman numeral-I) represents the raw signal. The seven steps within MPARRM yield the final denoised signal represented by the green trace (Roman numeral-VIII). Line noise and the stimulation artifact have been removed, while neural activity has been preserved.
