Figure 3.
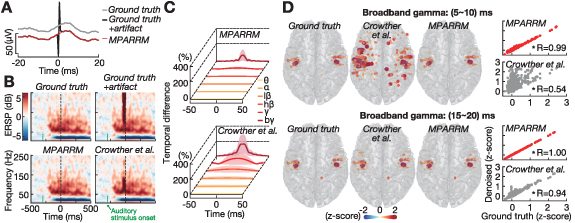
Validating MPARRM using synthetic signals with a representative pulse shape. (A) One representative single trial of ground truth signal (grey), ground truth signal added with saline stimulation artifact (black), and the denoised signal after applying MPARRM (red). We defined the ground truth signal as the SEEG signals recorded while performing a receptive speech paradigm. (B) Representative event-related spectral perturbation (ERSP) induced by an auditory stimulus for ground truth signal (top-left), ground truth signal added with saline stimulation artifact (time 0, top-right), the denoised signal after applying MPARRM (bottom-left), and the denoised signal after applying an interpolation-based stimulation artifact denoising method (bottom-right, Crowther et al 2019). (C) Temporal difference between the ground truth signal and the denoised signal within canonical frequency bands for MPARRM (top) and interpolation-based (bottom) denoising methods. (D) Left panel: topographic distribution of auditory-related broadband gamma response for ground truth signal (left) and the denoised signal for MPARRM (middle) and interpolation-based (right) denoising methods during two early-response periods. Right panel: correlation between the broadband gamma response of ground signal and denoised signal using MPARRM (upper, red) and interpolate (lower, grey) methods. Each dot indicates the averaged broadband gamma response during each response window of each electrode (* p 0.001, Pearson correlation).
