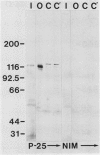
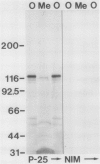
Abstract
A monoclonal antibody (Pea-25) directed to phytochrome from etiolated peas (Pisum sativum L., cv Alaska) binds to an antigenic domain that has been highly conserved throughout evolution. Antigenic cross-reactivity was evaluated by immunoblotting sodium dodecyl sulfate sample buffer extracts prepared from lyophilized tissue samples or freshly harvested algae. Pea-25 immunostained an approximately 120-kilodalton polypeptide from a variety of etiolated and green plant tissues, including both monocotyledons and dicotyledons. Moreover, Pea-25 immunostained a similarly sized polypeptide from the moss Physcomitrella, and from the algae Mougeotia, Mesotaenium, and Chlamydomonas. Because Pea-25 is directed to phytochrome, and because it stains a polypeptide about the size of oat phytochrome, it is likely that Pea-25 is detecting phytochrome in each case. The conserved domain that is recognized by Pea-25 is on the nonchromophore bearing, carboxyl half of phytochrome from etiolated oats. Identification of this highly conserved antigenic domain creates the potential to expand investigations of phytochrome at a cellular and molecular level to organisms, such as Chlamydomonas, that offer unique experimental advantages.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bártek J., Viklický V., Stratil A. Phylogenetically more conservative epitopes among monoclonal antibody-defined antigenic sites of human transferrin are involved in receptor binding. Br J Haematol. 1985 Mar;59(3):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier M. M., Greppin H., Pratt L. H. Characterization by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of monoclonal antibodies to pisum and Avena phytochrome. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):123–127. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier M. M., Pratt L. H. Comparative Phytochrome Immunochemistry as Assayed by Antisera against Both Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous Phytochrome. Plant Physiol. 1982 Sep;70(3):912–916. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.3.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier M. M., Pratt L. H. Immunopurification and initial characterization of dicotyledonous phytochrome. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):360–365. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels S. M., Quail P. H. Monoclonal antibodies to three separate domains on 124 kilodalton phytochrome from Avena. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):622–626. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt L. H. Comparative immunochemistry of phytochrome. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):203–209. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice H. V., Briggs W. R. Immunochemistry of phytochrome. Plant Physiol. 1973 May;51(5):939–945. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.5.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. O., Bonner B. A. Isolation of phytochrome from the alga mesotaenium and liverwort sphaerocarpos. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jun;42(6):762–766. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.6.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierstra R. D., Quail P. H. Native phytochrome: Inhibition of proteolysis yields a homogeneous monomer of 124 kilodaltons from Avena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5272–5276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig S. E., Ferrone S., Shevach E. M. Monoclonal antibodies directed against human Ia antigens detect an evolutionary conserved epitope on guinea pig Ia antigens with unique functional properties. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Jan;35(1):101–113. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]