Figure 7. Formalin fixation introduces a fixation artifact, whereby measurable β-Actin levels correlate with fixation time.
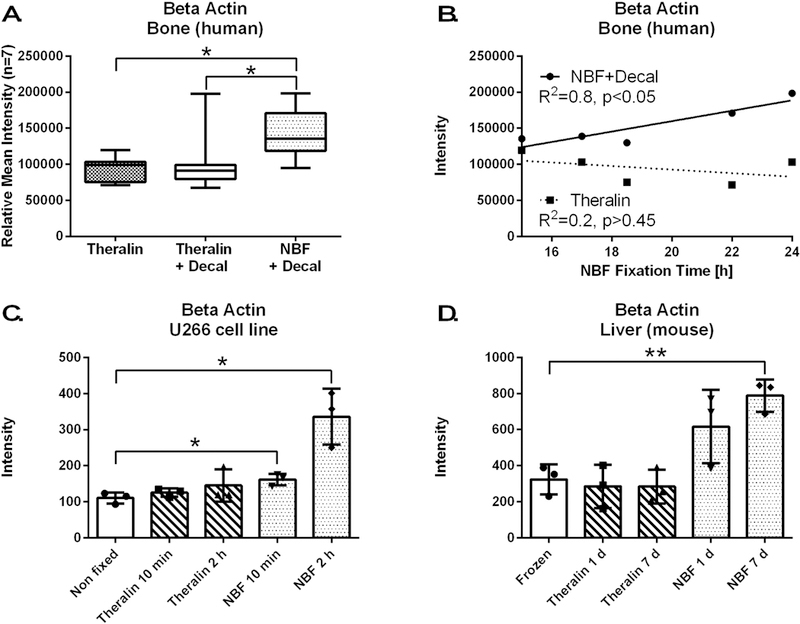
(A) β-Actin is increased following formalin fixation and decalcification of bone tumor samples compared to Theralin fixed or Theralin fixed and decalcified patient matched samples (n=7, laser-capture microdissected tumor cells, boxes = 25th to 75th percentile with whiskers going to the smallest and largest value, * p<0.05). (B) Subset of patient samples from (A) where exact fixation times were available (n=5) show a direct correlation between fixation time and the level of measurable β-Actin when fixed in formalin but not after Theralin fixation. (C) Fixing U266 cells with formalin for either 10 min or 2 h causes an increase in measurable β-Actin versus non-fixed cells. Theralin fixation does not alter β-Actin levels, independent of fixation time (±SD, * p<0.05). (D) Fixing mouse liver with formalin for 1 day or 7 days increases measurable β-Actin versus frozen tissue. Theralin fixation kept β-Actin levels at frozen tissue levels irrespective of fixation time (±SD, * p<0.01).
