Fig. 6 |. Pharmacological inhibition of HDAC1/HDAC2 using RBC1HI ameliorates sensory hypersensitivity signs of opioid withdrawal.
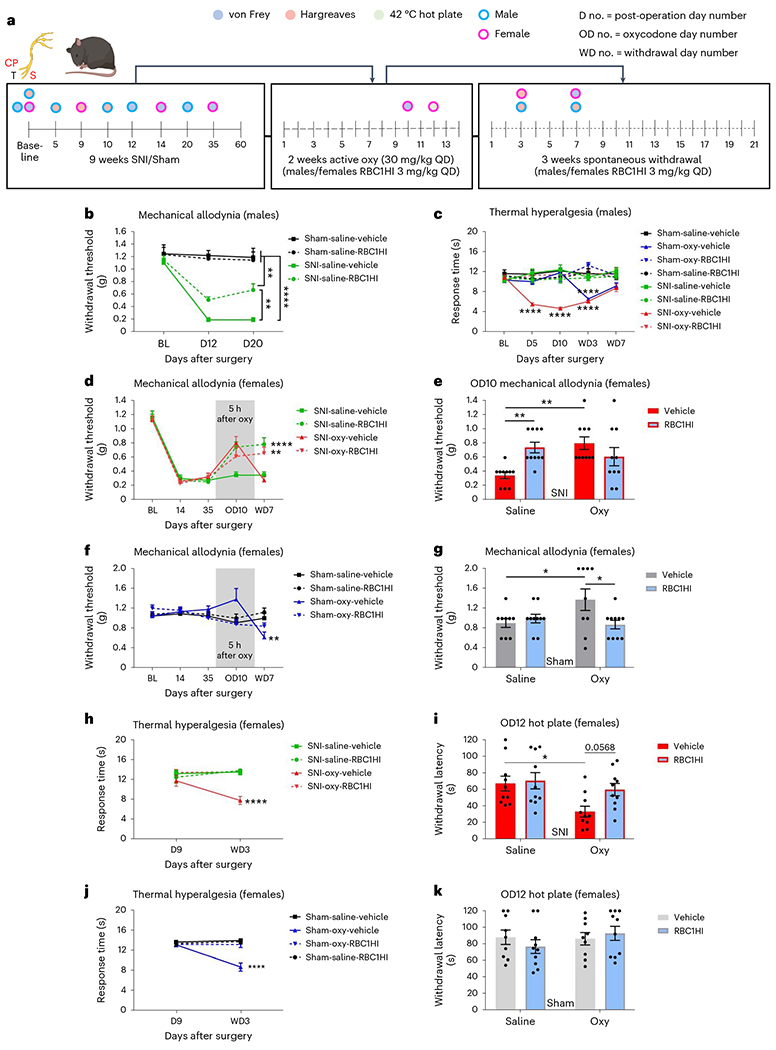
a, Schematic timeline of experimental design. b, RBC1HI promoted partial recovery from mechanical allodynia in groups of male mice with long-term SNI (Sham-Sal-Veh n = 7, Sham-Sal-RBC1HI n = 9; SNI-Sal-Veh n = 7, SNI-Sal-RBC1HI n = 10; repeated-measures two-way ANOVA interaction F6,58 = 5.858, P < 0.0001; Tukey’s multiple comparisons, day 20 SNI-Sal-Veh versus SNI-Sal-RBC1HI q = 5.12, d.f. = 87, P = 0.0027). c, Chronic treatment with 3 mg per kg body weight, RBC1HI prevented the development of oxycodone-induced hyperalgesia in male SNI groups exposed to chronic oxycodone. During spontaneous oxycodone withdrawal, inhibition HDAC1/HDAC2 prevented the induction of thermal hyperalgesia in both SNI and sham mice (Sham-Sal-Veh n = 7, Sham-Sal-RBC1HI n = 9; Sham-Oxy-Veh n = 8, Sham-Oxy-RBC1HI n = 10; SNI-Sal-Veh n = 7, SNI-Sal-RBC1HI n = 10; SNI-Oxy-Veh n = 8, SNI-Oxy-RBC1HI n = 7; repeated-measures two-way ANOVA interaction F28,232 = 5.01, P < 0.0001; Tukey’s multiple comparisons day 10 SNI-Oxy-Veh versus SNI-Oxy-RBC1HI q = 10.17, d.f. = 290, P < 0.0001; WD3 Sham-Oxy-Veh versus Sham-Oxy-RBC1HI q = 10.96, d.f. = 290, P < 0.0001; WD3 SNI-Oxy-Veh versus SNI-Oxy-RBC1HI q = 8.625, d.f. = 290, P < 0.0001). d,e, RBC1HI alleviated SNI-only and SNI-Oxy withdrawal-induced mechanical hypersensitivity on WD7. Five hours after Oxy administration on day 10, RBC1HI alleviated mechanical hypersensitivity in Sal-treated mice, but it did not affect the anti-allodynic response to Oxy, as Veh and RCB1H1 groups showed similar von Frey responses (SNI-Sal-Veh n = 10, SNI-Sal-RBC1HI n = 10, SNI-Oxy-Veh n = 10, SNI-Oxy-RBC1HI n = 10; repeated-measures two-way ANOVA interaction F12,144 = 4.531, P < 0.0001; Tukey’s multiple comparisons WD7 SNI-Oxy-RBC1HI versus SNI-Oxy-Veh q = 5.551, d.f. = 180, P = 0.0007; OD10 two-way ANOVA interaction F1,36 = 5.269, P = 0.0025; Sidak’s multiple comparisons SNI-Sal-Veh versus SNI-Sal-RBC1HI t = 3.112, d.f. = 36, P = 0.0072; SNI-Sal-Veh versus SNI-Oxy-Veh t = 3.589, d.f. = 36, P = 0.002). f,g, In sham mice, RCB1H1 prevented the analgesic effects of Oxy on mechanical thresholds and prevented the development of withdrawal-induced mechanical allodynia (Sham-Sal-Veh n = 9, Sham-Sal-RBC1HI n = 10, Sham-Oxy-Veh n = 9, Sham-Oxy-RBC1HI n = 10; two-way ANOVA interaction F1,34 = 5.269, P = 0.028; Sidak’s multiple comparisons OD10 Sham-Sal-Veh versus Sham-Oxy-Veh t = 2.517, d.f. = 34, P = 0.0332; OD10 Sham-Oxy-Veh versus Sham-Oxy-RBC1HI t = 2.754, d.f. = 34, P = 0.0187). h, RBC1HI pretreatment in this group of female mice also prevented the induction of thermal hyperalgesia after SNI with or without withdrawal in the Hargreaves assay (SNI-Sal-Veh n = 10, SNI-Sal-RBC1HI n = 10, SNI-Oxy-Veh n = 10, SNI-Oxy-RBC1HI n = 10; repeated-measures two-way ANOVA interaction F3,36 = 4.573, P = 0.0082; WD3 Tukey’s multiple comparisons SNI-Oxy-Veh versus SNI-Oxy-RBC1HI q = 7.742, d.f. = 72, P < 0.0001). i, When the same female Veh and RBC1HI SNI groups were tested in a 42 °C hot plate during active Oxy administration, RBC1HI ameliorated thermal hypersensitivity seen in SNI-Oxy mice (two-way ANOVA interaction F1,36 = 1.974, P = 0.1686; Sidak’s multiple comparisons OD12 SNI-Sal-Veh versus SNI-Oxy-Veh t = 2.899, d.f. = 36, P = 0.0126; OD12 SNI-Oxy-Veh versus SNI-Oxy-RBC1HI t = 2.277, d.f. = 36, P = 0.0568).j, RBC1HI effectively alleviated withdrawal-induced thermal hyperalgesia in Sham-Oxy animals (Sham-Sal-Veh n = 9, Sham-Sal-RBC1HI n = 10, Sham-Oxy-Veh n = 9, Sham-Oxy-RBC1HI n = 10; repeated-measures two-way ANOVA interaction F3,34 = 11.81, P < 0.0001; Tukey’s multiple comparisons Sham-Oxy-Veh versus Sham-Oxy-RBC1HI q = 9.016, d.f. = 68, P < 0.0001). k, There were no differences between Sham conditions in the 42 °C hot plate assay during active Oxy administration. Data indicate the mean ± s.e.m. Significance was calculated by means of two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001. QD, once a day; Veh, vehicle.
