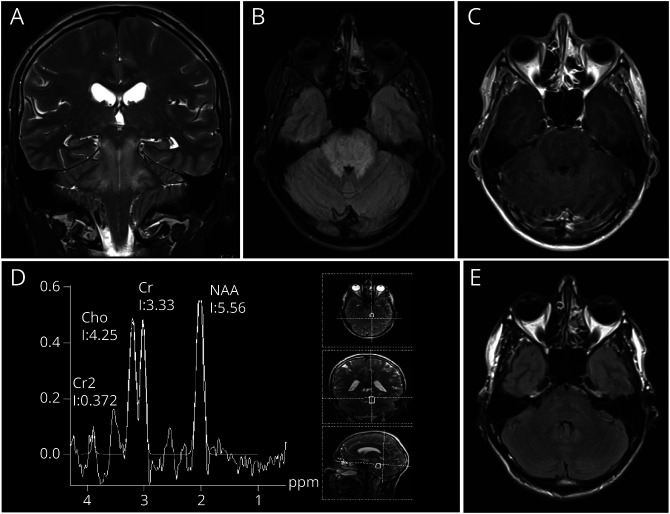
A 34-year-old patient presented with visual disturbance, headache, and vomiting. Physical examination revealed severe hypertension (RRsystolic 240 mm Hg) with secondary organ manifestations (hypertensive cardiomyopathy, renal failure, and hypertensive retinopathy). MR imaging showed T2/fluid-attenuated inversion recovery hyperintensities in the cerebellar peduncles, pons, and medulla oblongata with a space-occupying effect and point-shaped contrast enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images, suggestive for brainstem gliomas (Figure, A–C). MR spectroscopy indicated a reduced ratio of N-acetylaspartate (NAA)/creatine and NAA/choline, atypical for gliomas (Figure, D). CSF examination was unremarkable.
Figure. MR Imaging In a Patient With Isolated Brainstem Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome.
T2-weighted coronal images (A) and axial FLAIR images (B) reveal hyperintensities in the mesencephalon and pons. Contract-enhanced axial T1-weighted images show point-shaped pontine contrast enhancement (C). MR spectroscopy indicates a reduced ratio of N-acetylaspartate/creatine and N-acetylaspartate/choline (D). Twelve days later after antihypertensive therapy, only residual pontine FLAIR-hyperintensities persist (E).
Based on clinical and imaging examinations, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) with isolated brainstem involvement was diagnosed. Repeat MRI scan 12 days later after antihypertensive therapy showed only residual pontine T2 hyperintensities (Figure, E), supporting the tentative diagnosis.
Isolated brainstem involvement in PRES is rare (<4%).1 MR spectroscopy with a reduced ratio of NAA/creatine and NAA/choline without increased choline can help to differentiate between PRES and the differential diagnosis of a low-grade glioma.2
Author Contributions
L. Zerweck: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; study concept or design; analysis or interpretation of data; additional contributions (in addition to 1 or more of the above criteria). P. Bombach: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data. S. Hucker: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data. G. Tabatabai: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data. U. Ernemann: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; analysis or interpretation of data. B. Bender: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; study concept or design; analysis or interpretation of data.
Study Funding
The authors report no targeted funding.
Disclosure
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Go to Neurology.org/N for full disclosures.
References
- 1.McKinney AM, et al. Central-variant posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: brainstem or basal ganglia involvement lacking cortical or subcortical cerebral edema. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201(3):631-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sheikh-Bahaei N, Acharya J, Rajamohan A, Kim PE. Advanced imaging techniques in diagnosis of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES). Front Neurol. 2020;11:165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]