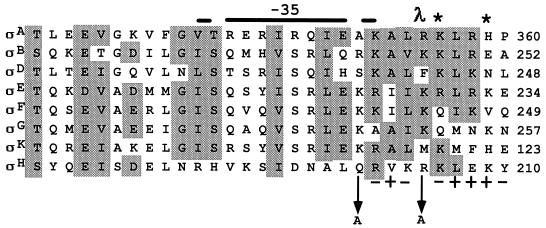
FIG. 1.
Amino acid alignment of the −35 recognition regions in the carboxyl terminus of sigma factors in B. subtilis. Conserved regions are shaded according to Sun et al. (16). The position number for the last amino acid shown in each sigma factor is indicated. ς70 of E. coli is not shown, but ς70 and ςA are almost identical in this region. Amino acid substitutions are indicated by the arrow from the wild-type amino acid to the altered amino acid. The + and − signs below the ςH sequence indicate the phenotypes of alanine substitutions at that amino acid in ςH. A + sign indicates an allele which produced a functionally wild-type ςH protein, and a − sign designates a completely inactive ςH protein. The λ indicates an amino acid substitution at 596 in ς70, R596H, which specifically suppresses the D38N mutation in λ cI (8, 9). The asterisk indicates amino acid substitutions in ςA (K356E and H359R) which specifically prevent transcription from Spo0A-dependent promoters (1).